DEI Promotion
To ensure success in today's rapidly changing business environment, we believe it is essential to attract diverse human resources and enable each employee to reach their full potential on the job.
Kyocera's Vision for DEI*
DEI is not meant to treat women; individuals with physical, intellectual, and emotional challenges; people from overseas; and members of the LGBTQ community as a special category but rather to describe all employees. Kyocera believes that everyone should be able to enjoy life and feel included, that ideas should be respected and accepted on the basis of their merits, and that the diverse potential of different people should be respected and encouraged. Kyocera regards DEI as an initiative intended to ensure the involvement and participation of all employees. Above all, Kyocera strives to understand how it can be an even more progressive company and how all employees can achieve a deeper understanding and acceptance of the true meaning and purpose of DEI.
The abbreviation of diversity, equity, and inclusion
Approaches to DEI
Considering opportunities for women in the workplace a core management theme at its domestic operations, Kyocera has initiated a variety of awareness programs since 2006 to promote corporate culture reforms and advance initiatives like balancing work and parenting. As a result, the number of women in management has increased. In 2019, the Diversity Promotion Division was established at our Japan headquarters to facilitate company-wide initiatives expanding diversity throughout the workforce. A Site-Specific Diversity Promotion Committee was also set up at each of Kyocera's major domestic plants and offices to lead local activities in response to site-level needs. Further, to cultivate a corporate climate that respects diversity, we provide guidance from top management, awareness education, and diversity training for managers, aiming to ensure a welcoming work environment for all.
Fostering a Corporate Culture that Espects Diversity
Transmitting the Message from our Top Management
Promoting diversity and inclusion is in line with Kyocera Corporation's Management Rationale, namely "to provide opportunities for the material and intellectual growth of all our employees, and through our joint efforts, contribute to the advancement of society and humankind." We also recognize it to be an important management issue if Kyocera is to achieve future growth. Accordingly, we communicate this message from our top management and share it with all our employees via media such as our company website, in-house intranet, and company newsletter.

Workplace Round-Table Discussions with Top Management, and Articles in our Company Magazine
Employees with diverse backgrounds, including foreign nationals, mid-career hires, employees with childcare or nursing care experience, employees with overseas work experience, and employees with disabilities, participate in discussions with top management on various issues under the theme of "Making Diversity a Strength of Kyocera. The content of their discussions are then shared in our company newsletter.
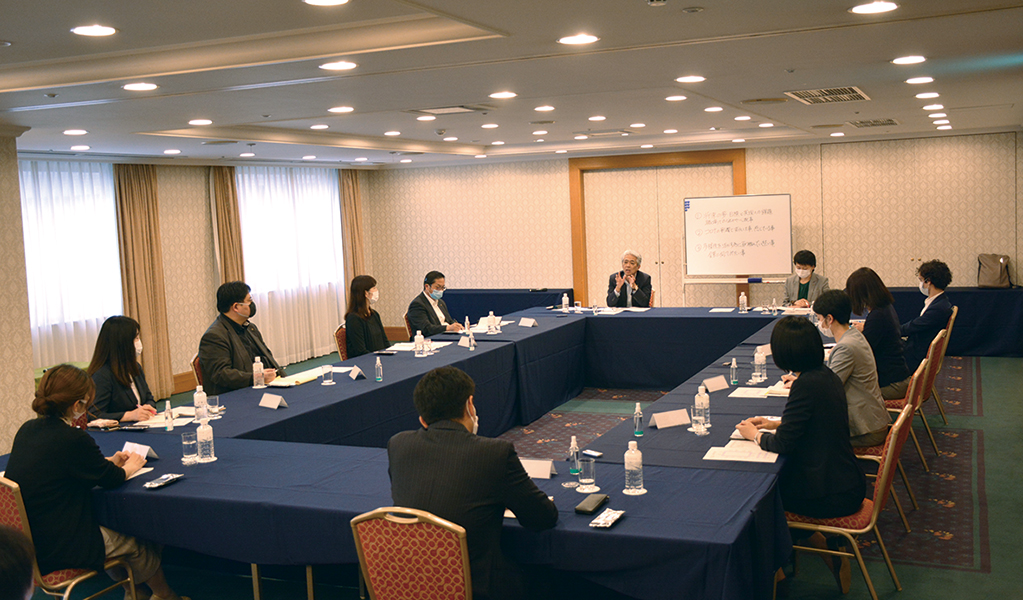

Educational and Awareness-Raising Activities for All Employees
As part of our efforts to foster a culture of respect for diversity, we conduct e-learning for all employees on topics such as "Unconscious Bias" and "Psychological Safety."
Educational and Awareness-Raising Activities for Managers
Diversity management training is run for management class employees. The aim is that they will acquire the mindset and management skills appropriate to an era of diversity.

Support Systems (to Balance Work and Child-Rearing, Family Nursing Care, Medical Treatment, etc.)
Kyocera Group companies in Japan provide a variety of support mechanisms, including a parental leave program and a shortened workday system, to help employees balance their careers and parenthood. Employees providing family nursing care support can apply to have working hours shortened or adjusted for an indefinite period. Since it is important to reduce employees' anxiety regarding the balance between work and family obligations, the Guidebook for Balancing Career and Nursing Care is also available on the company's intranet to provide relevant information to employees. A program allowing employees to take leave for up to two periods of as long as one year to allow for fertility treatment has been established as well.
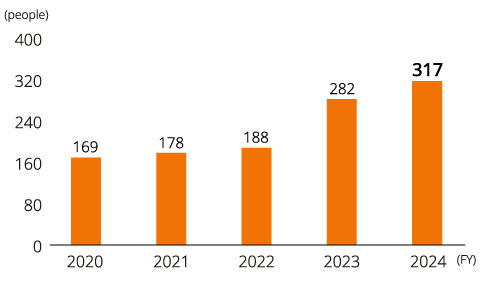
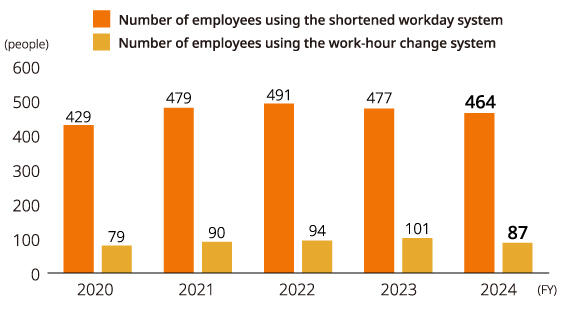
Use of Main Support Systems (Kyocera Corporation)
| Number of employees using the parental leave system | 317 |
| Number of employees using the shortened workday system | 464 |
| Number of employees using the work-hour change system | 87 |
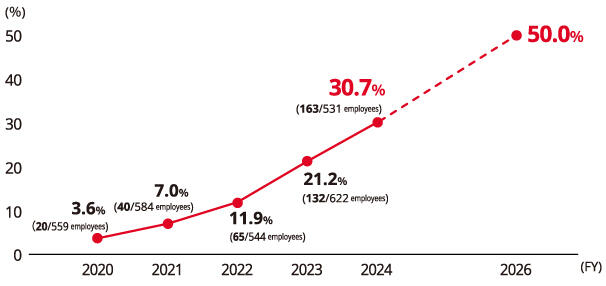
Promoting Childcare Leave
Kyocera has created a work environment in which all employees, both male and female, are able to take childcare leave more easily. To support men's participation in childcare, we hold roundtable discussions and workshops to promote understanding and guidance. Our approaches have led to an increase in the ratio of eligible male employees taking childcare leave from 3.6% in FY2020 to 30.7% in FY2024. We set a goal to achieve 50% by FY2026. Through management seminars and other efforts, we continue to create a work environment in which all employees feel comfortable taking childcare leave.

Ratio of Men Taking Childcare Leave (Kyocera)
Support Systems for Work-Life Balance
| System | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| Child-rearing | Paternity leave at birth system | Kyocera's paternity leave system allows employees to take up to 4 weeks of parental leave over a period of no more than 8 weeks after their spouse gives birth. (Leave can be divided into up to two installments) |
| Childcare leave system | Kyocera's childcare leave system allows employees to take leave in no more than two installments up to the day before the child's first birthday. Leave can also be extended until the child's second birthday, depending on the situation. Accumulated annual leave* can be used during part or all of an employee's childcare leave. *Accumulated annual leave: Employees are allowed to accumulate up to 20 days of expired paid annual leave. |
|
| Reduced working hours | The system is available to female employees from pregnancy or until the child completes sixth grade in elementary school. Up to 2 hours per day can be reduced. | |
| Work-hour change system | The system is available to female employees from pregnancy or until the child completes sixth grade in elementary school. Work start/end times can be adjusted by up to 90 minutes in total per day. | |
| Childcare assistance | The system is available until the employee's child completes sixth grade in elementary school. The maximum annual amount of subsidy is 200,000 yen per child. | |
| Child nursing care vacation | This system offers five vacation days per child per year, or 10 days for two or more children, available until the employee's child completes sixth grade in elementary school. Vacation is also available by the day or by the hour. | |
| Nursing care | Family nursing care leave system | The system is available to employees providing family nursing care. A one-year of leave is acceptable in total per care receiver. (Leave can be divided into several times.) |
| Shortened workday system | No fixed duration: work can be shortened up to two hours per day. | |
| Work-hour change system | No fixed duration: work can be shortened up to two hours per day. Work start/end times can be adjusted by up to 90 minutes in total per day. | |
| Family nursing care vacation | Employees providing nursing care are eligible for five days of leave in total per year per care recipient and ten days in the case of two or more care recipients. Leave is also available by the day or by the hour. | |
| Medical treatment | Shortened workday system | Working hours can be shortened by up to two hours per day if deemed necessary by the company based on the diagnosis of a doctor or the judgment of an industrial physician. |
| Work-hour change system | Employees are allowed to adjust the start of workday by up to 90 minutes in total per day if deemed necessary by the company based on the diagnosis of a doctor or the judgment of an industrial physician. | |
| Support system for fertility treatment | Our Fertility Treatment Support system allows employees to take two periods of leave for up to one year. Accumulated annual leave by the hour is also available. | |
| Other | Come-back entry system | The system allows employees who left Kyocera for reasons such as child-rearing, family nursing care, or other personal reasons, to re-enter the company. Former Kyocera employees are eligible for this system within seven years after their departure. When a former employee applies for re-entry, Kyocera's job openings and the applicant's desire will be reviewed for appropriateness, and their re-employment will be approved if they are matched. |
| Annual paid vacation system on an hourly basis | Employees are allowed to take up to five days (40 hours) of leave in hourly units up to 7 hours per day from the provided annual paid vacation. | |
| Accumulated annual leave | The system allows employees to take paid leave by the hour (up to three hours per day) for the purposes of family/child care, parenting, participation in the school events of their children, or their own medical treatment. | |
| System of leave in the case of spouse transferring overseas | Employees who are unable to continue their duties as a result of their spouse being transferred overseas may take leave for a maximum of five years. |
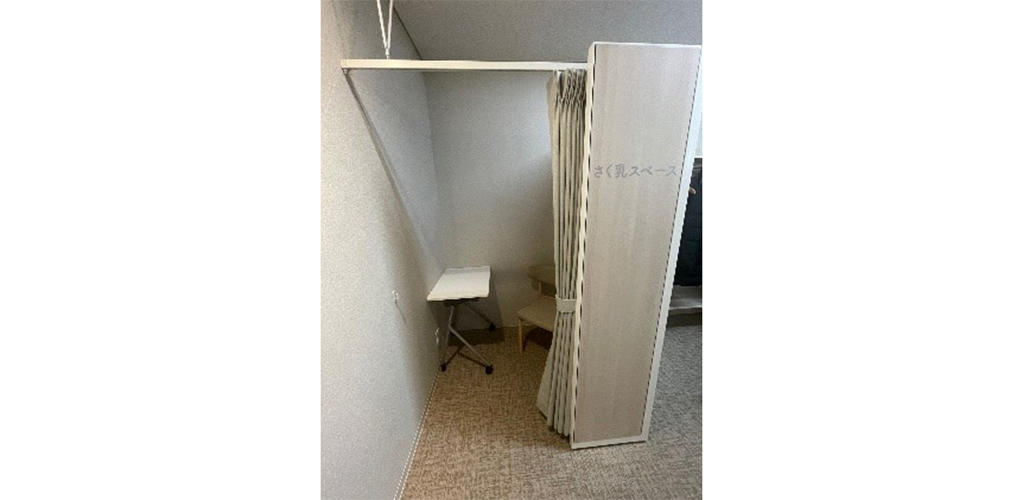



Creating a Comfortable Workplace Environment for All Our Employees
Approaches to Understanding LGBTQ Issues
Kyocera is making efforts to raise employee awareness of LGBTQ issues and create a comfortable work environment for all. We created SOGI 2-LGBTQ Guidelines and have revised our in-house policies to include recognition of same-sex partners as spouses, and the prohibition of conduct, by word or deed, that disadvantages other employees based on their sexual orientation or gender identity. We also provide seminars, both to the general workforce and to employees in general affairs and human resources, to ensure that Kyocera works as an ally to members of the LGBTQ community. In recognition of these efforts, work with Pride, an association that promotes diversity and inclusion to protect members of the LGBTQ community and other sexual minorities, awarded Kyocera the Gold Rating, the highest specified by its PRIDE Index, for two consecutive years.



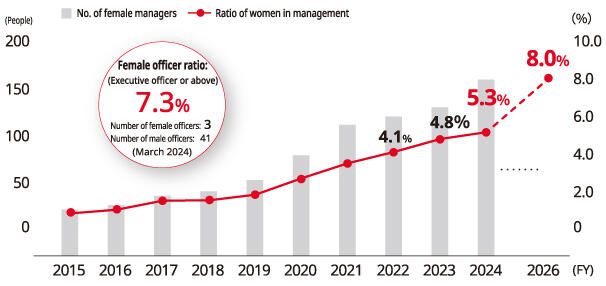
Improving Gender Representation
By FY2026, Kyocera Corporation set the goal of having 8.0% of its management positions held by women. The company is improving training opportunities for management candidates and actively promoting capable women to managerial positions. Furthermore, Kyocera established the Positive Action Promotion Committee, a body comprising representatives from each business segment, to focus on employee engagement for women in each department and provided a wide range of external training programs. As of FY2024, Kyocera Corporation had 161 female managers (5.3%) and 1 female director and 2 female executive officers (7.3%) within its executive team. The company will continue to seek new ways of promoting the participation of women throughout the Group.
Transitions in the Numbers and Ratios of Female Managers (Kyocera)
Reference: Average ratios of management positions held by women in Japan, by industry -- The average ratio in electronic component, device and circuit manufacturing, electrical machinery and appliance manufacturing, and information and communication equipment manufacturing industries was 3.6% (period: July 1, 2024, to June 30, 2025)
Source: "Average values" in standards relating to certification systems based on the Act on the Promotion of Female Participation and Career Advancement in the Workplace, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (June 2024)
Implementation of Female Leaders' Training and Lecture Meetings
Targeting female employees, we invite external lecturers to conduct lecture meetings that incorporate mindset and skill improvement elements that will be needed by female employees to succeed as future leaders. These are opportunities to build networks that cross over locations and departments and obtain new perspectives and realizations for conducting work. Moreover, regarding female empowerment as part of our management strategy, we also hold lecture meetings to deepen understanding to ensure that all employees, including men, engage in initiatives for female empowerment.

Female Employee Statistics
As of March 31, 2024
| Percentage of female employees* | 19.5% (Number of female employees:4,142 / Total number of employees:21,156) |
| Percentage of female managers* | 5.3% (Number of female managers: 161 / Total number of managers: 3,054) |
| Percentage of management positions in profitable divisions held by women* |
3.6% (Number of female managers: 71 / Total number of managers: 1,990) |
| Percentage of women in (Executive positions and above) | 7.3% (Number of female executives: 3 / Total number of executives: 41) |
Kyocera Corporation
Equal Pay
| Male to female earnings ratio for managers | Male: 100 Female: 99.4 |
| Male to female earnings ratio for employees | Male: 100 Female: 72.0 |
Employment for People with Disabilities
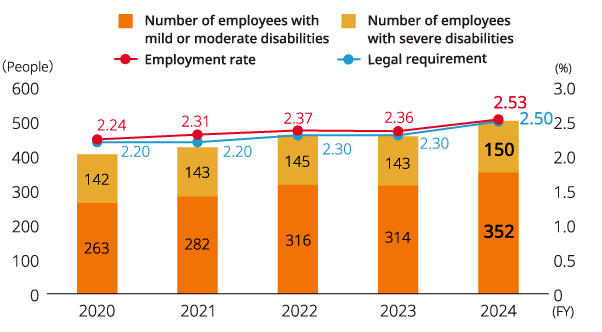
Kyocera is committed to the hiring of people with disabilities and to promoting their continued employment. Employees with disabilities hired by Kyocera are assigned with consideration so that their jobs and workplaces match their capabilities. As of June 2024, the rate of employees with disabilities was 2.53% (2.30% the previous year). Kyocera intends to develop specific action plans and actively employ people with disabilities to enhance the ratio of employees with disabilities.
Number/Employment Rate of Employees with Disabilities
Message from Diversity Promotion Division
Making Diversity a Strength for Kyocera
Management based on the bond of human minds is a principle that Kyocera has kept since its founding. Employees with different experiences and values have cared for and helped each other like a family, striving together with the goal of making Kyocera a wonderful company. This view is consistent with diversity & inclusion, a concept which aims to pursue respect for the human rights and diverse personalities of all individuals. Implementation of this concept will result in the happiness of all employees, the growth of the company, and contribution to the development of society; this represents a key aspect of management at Kyocera.
In the over 60 years since its establishment, Kyocera has become a global corporation of abundant diversity, where people endowed with wide-ranging knowledge and skills come together. To leverage these assets and realize growth that continues into the future, we believe that it is necessary to fully bring out the abilities of each and every member of our diverse workforce and convert them into Kyocera's strengths and innovations. Now above all, it is time to return to the challenger spirit of our founder and vitalize communication that goes beyond organizational and national boundaries so that we can generate synergies of diversification, further extend our business, and contribute to society.
Against this background, the Diversity Promotion Division was established in 2019. We aim to be a dynamic and attractive company that challenges and grows continuously by creating a work environment for diverse human resources to work with satisfaction, respecting the individuality and values of each employee. The entire company is working together to promote "Diversity and Inclusion" in the belief that it will enable us to move closer to realizing Kyocera Corporation's Management Rationale, namely "To provide opportunities for the material and intellectual growth of all our employees, and through our joint efforts, contribute to the advancement of society and humankind."
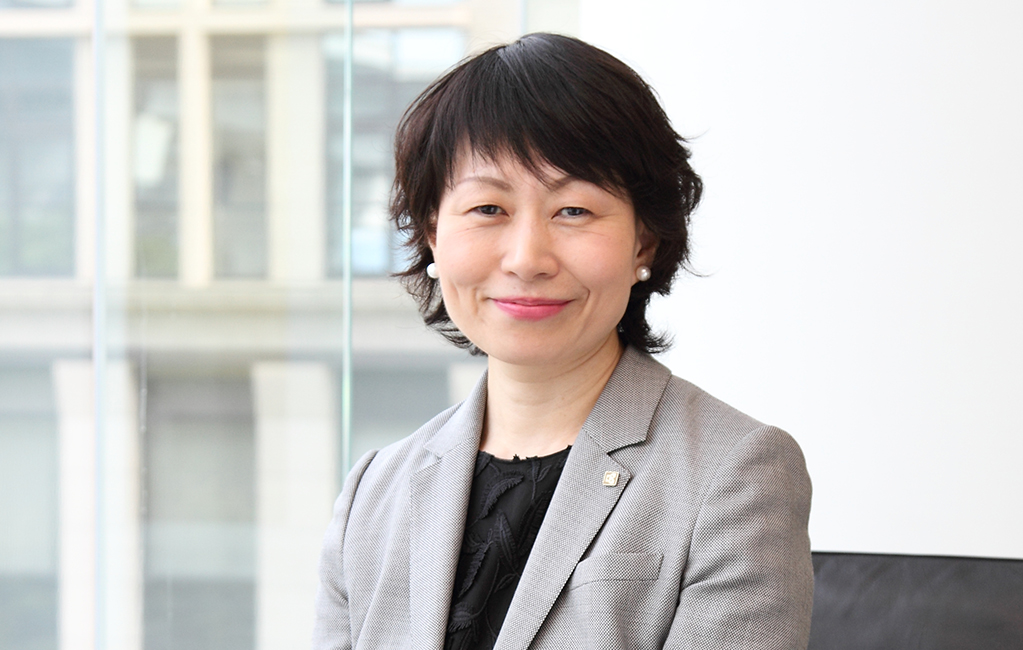

General Manager of Corporate Communications Division
and Diversity Promotion Division
Eri Yoshikawa
Creating a Comfortable Workplace Environment
The Kyocera Group maintains a fundamental management rationale to provide opportunities for the material and intellectual growth of all our employees, and through our joint efforts, contribute to the advancement of society and humankind. To realize Kyocera's Management Rationale to grow and develop the company on sustainable basis, it is essential to maximize employees' abilities. To continue growing in the current rapidly changing global business environment, we believe that attracting more diverse employees and letting every employee fully demonstrate their abilities are important.
Personnel System
The Kyocera Group is constantly working to create a range of innovative human resource initiatives based on its human resources rationale. Through these initiatives, we aim to create a workplace environment where all employees can feel pride in the company and satisfaction in their work. Furthermore, we aim to create a workplace culture where everyone can share their joy and challenges, and contribute to achieving our company's management rationale.
Workstyle Reforms
Implementing Flexible Work Systems
Kyocera Corporation has introduced telecommuting to allow remote work. We are also promoting videoconferencing and virtual meetings using cloud services throughout the Kyocera Group. Moreover, our style of work is becoming increasingly diverse according to job functions and responsibilities. Encouraging the adoption of workstyles that suit the characteristics of jobs, Kyocera Corporation has introduced a flextime system in an effort to boost the company's total productivity.
Optimizing Workstyles
To improve productivity and deter long work hours, Kyocera Corporation has set limits on labor hours for its department and section managers. We are also making workflow enhancements that optimize labor to produce results in less time.
Developing Human Resources with Diverse Skillsets
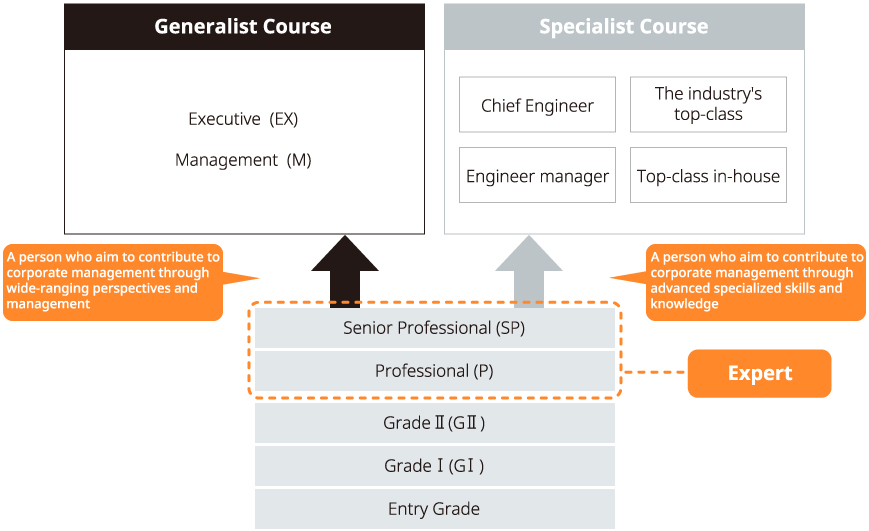
Advanced Specialty Course (Certification of Group Principal・Principal Engineer)
In Japan, Kyocera Corporation has also set up "Advanced Specialty Course " using qualification grades as a system to recognize and treat human resources with advanced skills. Qualified employees can be certified, for example, as a "Group principal engineer" or "Principal engineer." Further, in Senior Professional and Professional qualifications, employees who maximize their high-level expertise and practical skills contributions can be certified as "Experts."
- Group principal engineer: Individuals who have top-class expertise within their industry and contribute to the company
- Principal engineer: Individuals who have top-class expertise within the Group and contribute to their department
Expert System
Employees who have a high level of expertise and practical skills in their SP (Senior Professional) and P (Professional) qualifications and who can be expected to achieve even greater results by entrusting their work execution methods and time allocation to themselves are certified as "experts" covered by overtime compensation guarantees in the same way as managers and supervisors.
《System of Qualifications: Generalist Course and Advanced Specialty Course》
Communication Approaches
Regulations Review Project
Employees’ needs and lifestyles become diversified along with changes in the social climate. Labor and management are therefore working together on checking systems and standards to ensure they are always appropriate, fair and impartial.
Labor and Management Exchange Conference
Meetings of labor and management representatives are held each month in Kyocera plants and offices. The purpose of the meetings is to verify working conditions for employees and the workplace environment, and to actively exchange views on matters needing improvement, among other issues.
People Analytics
Kyocera uses people analytics to solve HR issues and improve HR policies to enable more appropriate decision-making through the use of HR data.
Initiatives
| Item | Summary |
|---|---|
| Identifying Risks to Retention Improvement | By analyzing the circumstances of resignations, we strive to identify factors that contribute to resignations and improve the work environment. |
| Organizational Network Analysis | The workplace vitality assessment enables activities to improve workplace vitality and engagement. |
| Data Analysis to Resolve HR Issues and Improve HR policies | Analysis of supervisors' competence which encourage their subordinates to take on new initiatives to foster a better, more dynamic work environment. |
Analysis Result Examples
Initiatives to Improve Workplace Vitality and Engagement
The Kyocera Group (in Japan) regularly conducts an employee engagement survey. The survey is conducted using a five-point scale (five being the highest possible score) on questions concerning attitudes toward work, workplace openness, participation in management, and trust in the company, etc. The results are analyzed on an organization-by-organization basis to diagnose the vitality of each workplace. Using the survey results as a reference indicator, division and team leaders lead workplace improvement activities to enhance vitality at each workplace.
| Survey Results for FY2024 | |
|---|---|
| Number of People Surveyed | 29,781 |
| Number of Respondents (Response Rate) | 27,886 people (93.6%) |
| Number of Questions | 74 questions |
| Language | Japanese only |
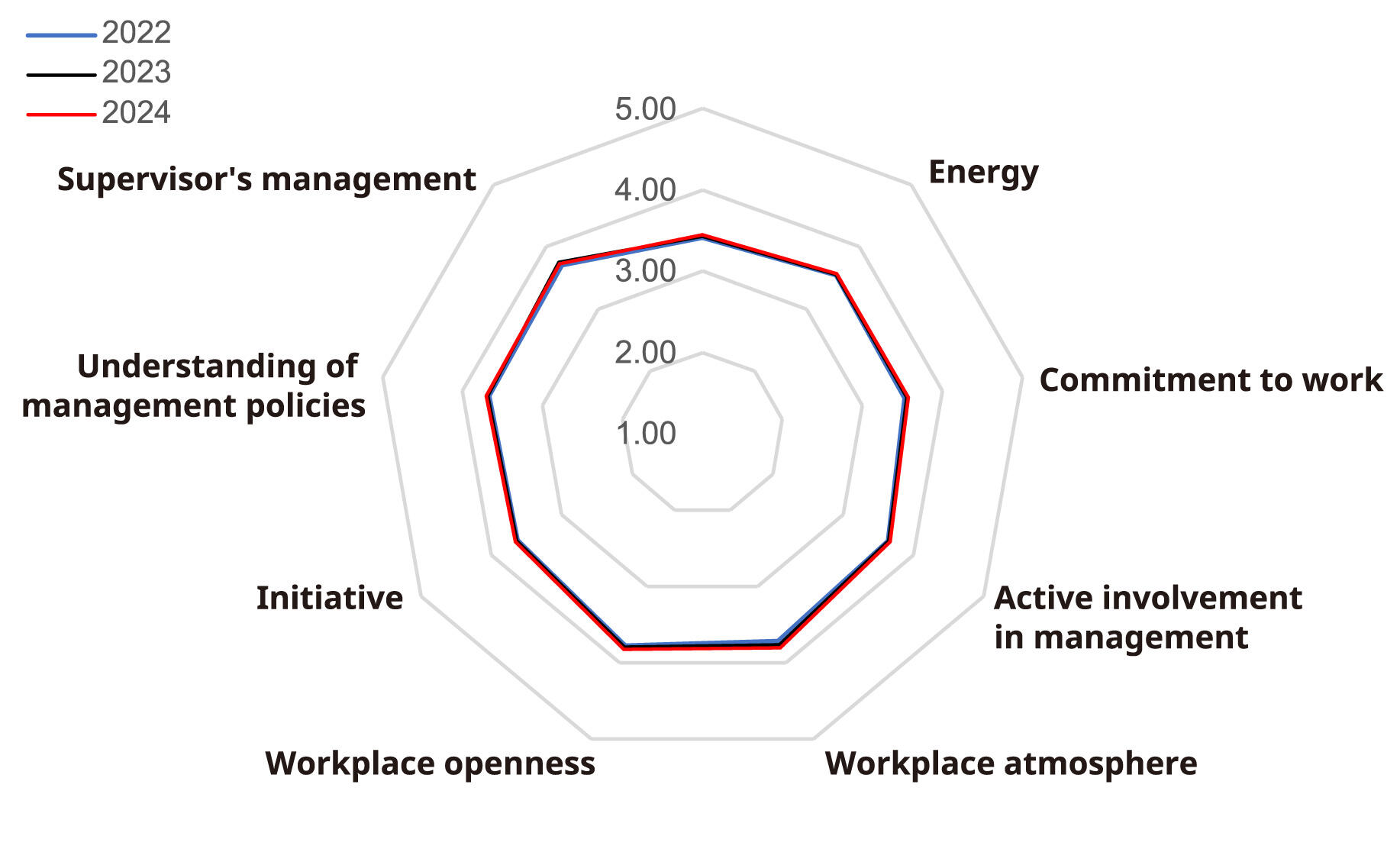
FY2022・FY2023・FY2024 Results of Workplace Vitality Assessment
| Item | Kyocera Group Average (FY2022) |
Kyocera Group Average (FY2023) |
Kyocera Group Average (FY2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 3.41 | 3.43 | 3.45 |
| Commitment to work | 3.55 | 3.56 | 3.57 |
| Active involvement in management | 3.53 | 3.55 | 3.57 |
| Workplace atmosphere | 3.64 | 3.65 | 3.67 |
| Workplace openness | 3.72 | 3.77 | 3.81 |
| Initiative | 3.78 | 3.80 | 3.83 |
| Understanding of management policies | 3.63 | 3.64 | 3.66 |
| Supervisor's management | 3.67 | 3.69 | 3.70 |
| Trust in the company | 3.70 | 3.75 | 3.73 |
Percentage of Employees Who Gave a Rating 4 or Higher
| FY2022 | 51% |
|---|---|
| FY2023 | 52% |
| FY2024 | 53% |
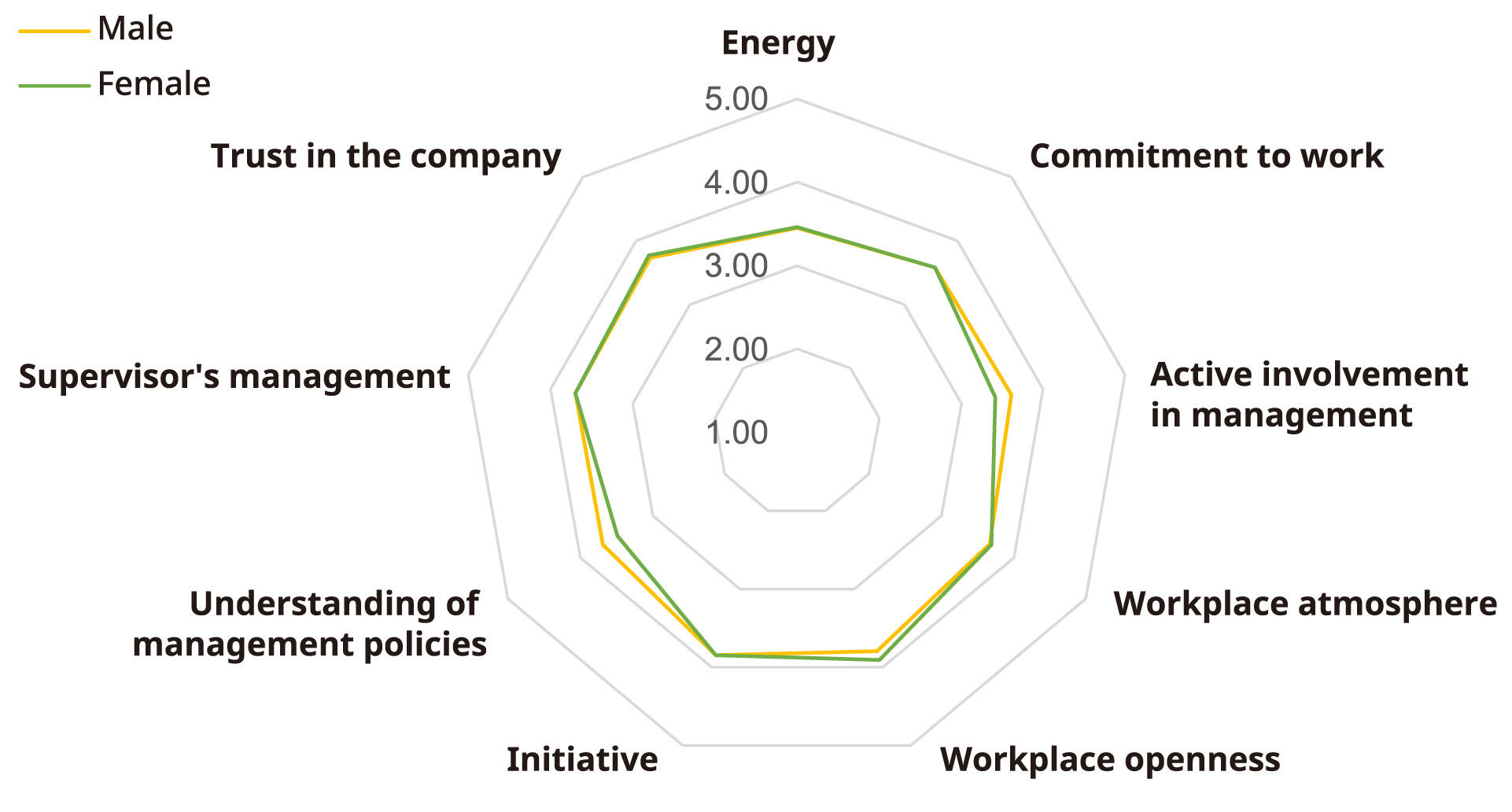
Results of the FY2024 Workplace Vitality Assessment (by Gender)
| Item | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | 3.45 | 3.46 |
| Commitment to work | 3.58 | 3.58 |
| Active involvement in management | 3.61 | 3.41 |
| Workplace atmosphere | 3.67 | 3.69 |
| Workplace openness | 3.79 | 3.90 |
| Initiative | 3.84 | 3.84 |
| Understanding of management policies | 3.69 | 3.49 |
| Supervisor's management | 3.70 | 3.70 |
| Trust in the company | 3.73 | 3.77 |
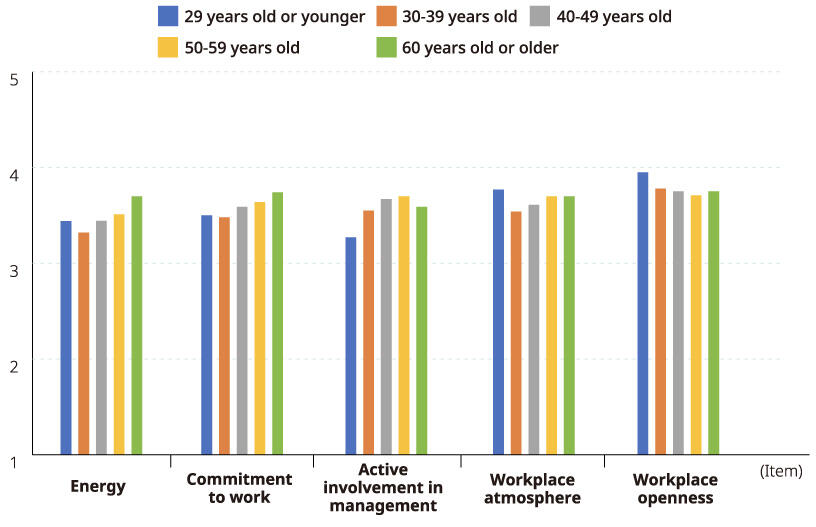
Results of the FY2024 Workplace Vitality Assessment (by Age Group)
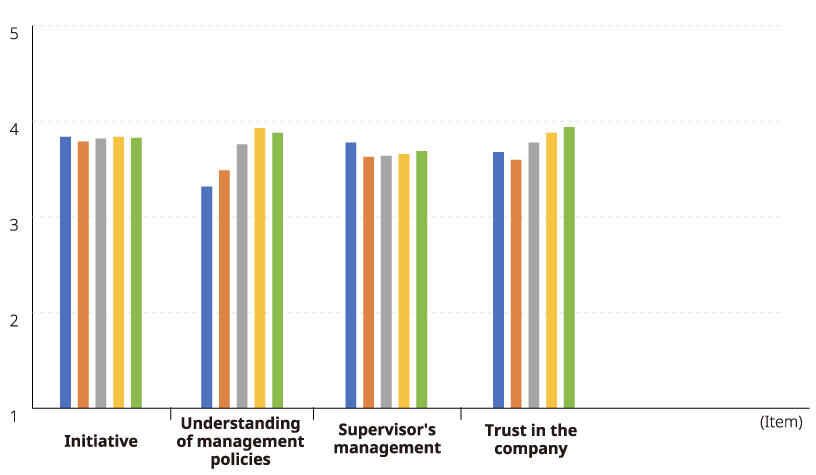
| Item | 29 years old or younger | 30-39 years old | 40-49 years old | 50-59 years old | 60 years old or older |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 3.44 | 3.32 | 3.44 | 3.51 | 3.70 |
| Commitment to work | 3.50 | 3.48 | 3.59 | 3.64 | 3.74 |
| Active involvement in management | 3.27 | 3.55 | 3.67 | 3.70 | 3.59 |
| Workplace atmosphere | 3.77 | 3.54 | 3.61 | 3.70 | 3.70 |
| Workplace openness | 3.95 | 3.78 | 3.75 | 3.71 | 3.75 |
| Initiative | 3.83 | 3.78 | 3.81 | 3.83 | 3.82 |
| Understanding of management policies | 3.31 | 3.48 | 3.75 | 3.92 | 3.87 |
| Supervisor's management | 3.77 | 3.62 | 3.63 | 3.65 | 3.68 |
| Trust in the company | 3.67 | 3.59 | 3.77 | 3.87 | 3.93 |
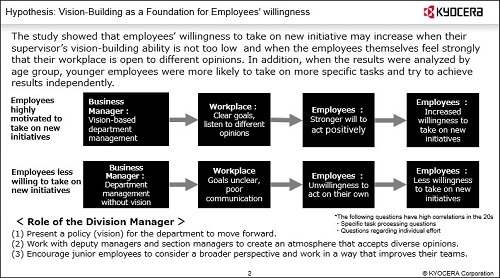
Supervisors Who Encourage Subordinates to Take on New Initiatives
We are analyzing the influence of the division manager's leadership style and workplace conditions on employees' willingness to take on new initiatives and how the degree of influence varies by employee demographics. The analysis showed that, across all generations, the willingness decreased when the division manager's vision-creation ability was low and increased when the workplace was more accepting of different opinions. Therefore, the training for new section managers addresses workplace openness, and training for division managers addresses the importance of presenting a vision, or "what they want to be," in running the division. By incorporating the results of this analysis into management training and other programs, we are fostering a more dynamic work environment.

Corporate Motto / Management Rationale / Management Philosophy
- Top Management Message
- Sustainability Management
- Kyocera Group CSR Guidelines
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Environmental Safety Policy / Targets and Promotion System
- Measures to Fight Climate Change -Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations-
- Water Risk Response
- Contribution to the Circular Economy/ Approaches to Waste Reduction
- Initiatives to Prevent Environmental Pollution
- Biodiversity Conservation
- Environmentally Friendly Products / Green Procurement
- Environmental Communication
- A History of Our Environmental Protection Activities
Social Citizenship Initiatives
- The Kyocera Group Human Capital
- Respect for Human Rights
- DEI Promotion
- Occupational Safety
- Occupational Health, Safety, and Fitness Initiatives
- Supply Chain Management
- Approaches to Raising Quality and Customer Satisfaction Levels
- Social Contribution Activities
- Academic Advancement and Research
- Support for Culture and the Arts
- International Exchanges and Collaboration
- Environmental Protection Activities
- Local Community Activities
- Social Welfare Activities
- Contributions to Society through Business Activities

