Contribution to the Circular Economy/ Approaches to Waste Reduction
All Kyocera Group corporate activities are based on our corporate motto, "Respect the Divine and Love People," and our three pillars for "LIVING TOGETHER": coexistence with society, coexistence with the global community, and coexistence with nature.
We aim to establish a recycling system that reduces the consumption of natural resources with the goal of protecting the global environment and realizing a sustainable society.
Contribution to the Circular Economy
The Circular Economy Concept
Laws and regulations have been established and standardized with increasing frequency throughout the world. The EU has pioneered the implementation of circular economy action plans, and has actively set goals to reduce the total amount of waste incineration and landfill. In line with these movements, the Kyocera Group established a new division to build a system for the reuse of a wide variety of waste produced at the factories in recycled materials with the goal of achieving zero waste discharge.
Approaches to the Circular Economy
Environmental-load reduction for packaging materials
The Kyocera Group promotes the reduction of material use and utilization of recycled resources through the design and development of packaging materials.
Designs for resource-savings
The Kyocera Group contributes to the reduction of environmental load while maintaining functionality through decreased material use by adopting new-style folding boxes.
Recycling Waste PET Film into Product Parts
Waste PET film generated during the production process of ceramic products has been difficult to reuse due to attached substances in the process, so it has traditionally been incinerated (thermal recycling), which posed a challenge of large CO2 emissions. To address this challenge, we were the first in the industry to establish* technology to convert waste PET film into recycled PET material and upcycle it (reuse for higher-value applications) into parts for multifunction devices and printers. Rather than relying on incineration, by collecting and reusing these materials to create new products, we reduce waste and CO2 emissions while also reducing the use of new plastic. This is an excellent example of resource circulation within the Group, and we are advancing initiatives aiming to expand to exterior parts and increase the proportion of recycled materials in the future.
As of September 30, 2024, according to KYOCERA Document Solutions Inc.

Circular system for multifunction peripherals (MFPs) and printers
Kyocera Document Solutions Inc. has established a circular business cycle encompassing product design, production, collection, and recycling.
Environmentally conscious designs
The Kyocera Group has implemented long-life designs, 3R (reduce, reuse, recycle) designs, and low energy-consumption designs, and has strived to reduce environmental load since the initial stage of product development in accordance with the Environmentally Conscious Design Standards.
Post-consumer recycled (PCR*) plastic utilization
The Kyocera Group has implemented PCR for products and toner containers. The Group set the goal of 1% or more PCR utilization in 2023, 5% or more PCR utilization and the use of recycled materials at 50% of all MFPs in 2024.
PCR:Plastic materials that have been collected from consumers after use and recycled into new plastic products.
From Collection to Reuse
We collect used MFPs and printers and promote their reuse at both the material and product levels in selected regions. By enhancing designs that facilitate easier refurbishment, we aim to expand reuse across our product portfolio.
Recycling of used mobile phones
The Kyocera Group makes effective use of the valuable resources contained in mobile phones as a way of reducing environmental impact.
Mobile Recycling Network (MRN)
The Kyocera Group promotes collection and recycling activities in cooperation with other companies through the Information and Communication Network Industry Association of Japan (CIAJ). Mobile phones are collected nationwide by collection centers for recycling to prevent environmental destruction by mining.
Recycling of machine tools
The Kyocera Group contributes to zero emissions at plants through its recycling program for used chips and chip cases from machine tools.
Chip case recycling program
The Group carries out collection and recycling activities for used carbide materials and chip cases aiming to achieve both improvement of productivity and sustainability, and contribute to the reduction of environmental load.
Developing Proprietary Technology to Recover Rare Earths from Fuel Cells
Kyocera is working on recycling that involves collecting used fuel cells and extracting rare earths (yttria) from the cell stack, which is the heart of the fuel cell. We have been conducting research with Kagoshima University and have established proprietary technology to dissolve the ceramic components of the cell stack in a special liquid and separate and recover yttria. We aim to recycle rare earths as much as possible and are advancing the practical application of a resource recovery process that is viable both in terms of cost and technology.



ENE・FARM is a registered trademark of ENEOS Corporation, Osaka Gas Co., Ltd., and Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd.
Recovering Carbon Through Carbonization of Waste Sludge
Sludge generated during the manufacturing process contains carbon components that originally have value as energy and materials, but processing has been difficult, and this material has traditionally been disposed of by incineration or landfill. Kyocera is working on technology development to carbonize this sludge and reuse it as a carbon material such as activated carbon. This initiative shows strong potential as a way to simultaneously achieve not only waste reduction but also suppression of CO2 emissions and resource circulation.

Approaches to Waste Reduction
Resource recovery rate
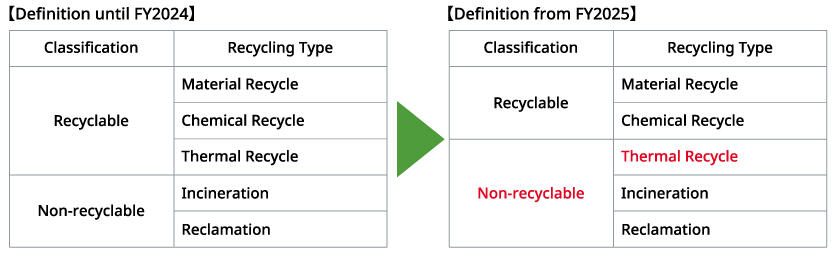
Until FY2024, Kyocera defined thermally recycled wastes as recyclable wastes. From FY2025, in order to promote the circulation of plastics and other resources, Kyocera defines thermal recycled wastes as non-recyclable wastes and strives for reduction. In FY2025, the Kyocera Group advanced waste reduction by setting individual targets at five production sites that generate more non-recyclable wastes than other locations do. However, from FY2026, the scope will be expanded to include Kyocera's domestic production sites, Kyocera Document Solutions' production sites, KYOCERA Thailand, and KYOCERA Vietnam. At the same time, the company will shift to setting absolute volume targets. The Group continues striving to realize a sustainable society.
| Targets for FY2025 |
|
|---|---|
| Achievements in FY2025 |
|
| Targets for FY2026 |
|
|---|
According to the previous definition (including thermal recycling as a category of recyclable waste), recycling ratio by the Kyocera Group (Japan production sites) in FY2025 was 99.5%.
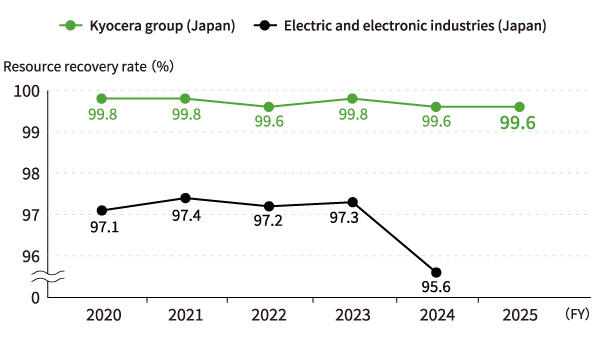
The definition of the recycling rate (%) is "1 - final disposal amount/discharge amount" x 100.
Recycling rates have not been provided for the four main electric and electronic goods industry bodies for FY2025 and have been omitted.
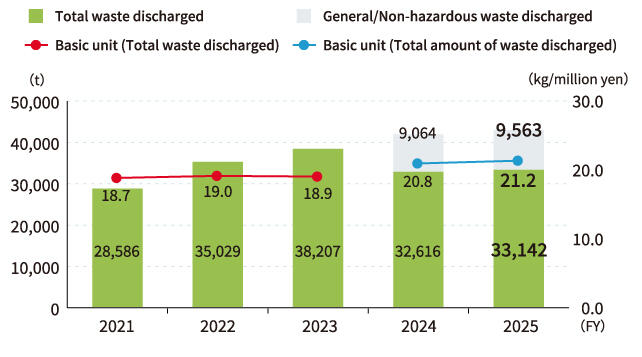
Waste Discharge
The Kyocera Group manages the amount of waste discharged and disposed of in landfills from the viewpoint of resource recycling. The Kyocera Group evaluates the waste discharge rate and waste treatment cost rate, and indicates the locations with high waste risk.
As a result of the FY2026 waste risk assessment, there were 11 sites with high waste risk, and the total amount of waste discharged was 28,923 tons, accounting for 67% of the total amount of waste discharged in FY2025.
| Targets for FY2025 |
|
|---|---|
| Achievements in FY2025 |
|
| Targets for FY2026 |
|
|---|
Range of Waste to be Recycled
FY2021~2023:[Japan] Industrial Waste+ Specially Controlled Industrial Waste [Overseas] hazardous waste
FY2024~:[Japan]Industrial Waste+ Specially Controlled Industrial Waste + General Waste [Overseas]Hazardous waste+ Non- hazardous waste
The basic unit is calculated based on the Range of Waste to be Recycled. (Until FY2023, it was calculated from the amount of waste generated; from FY2024 onward, it is calculated from the total amount of waste generated, including general waste and non-hazardous waste.)
Data in FY2023,2024 has been updated to improve the accuracy of data aggregation at some locations.
Cases of Waste Reduction
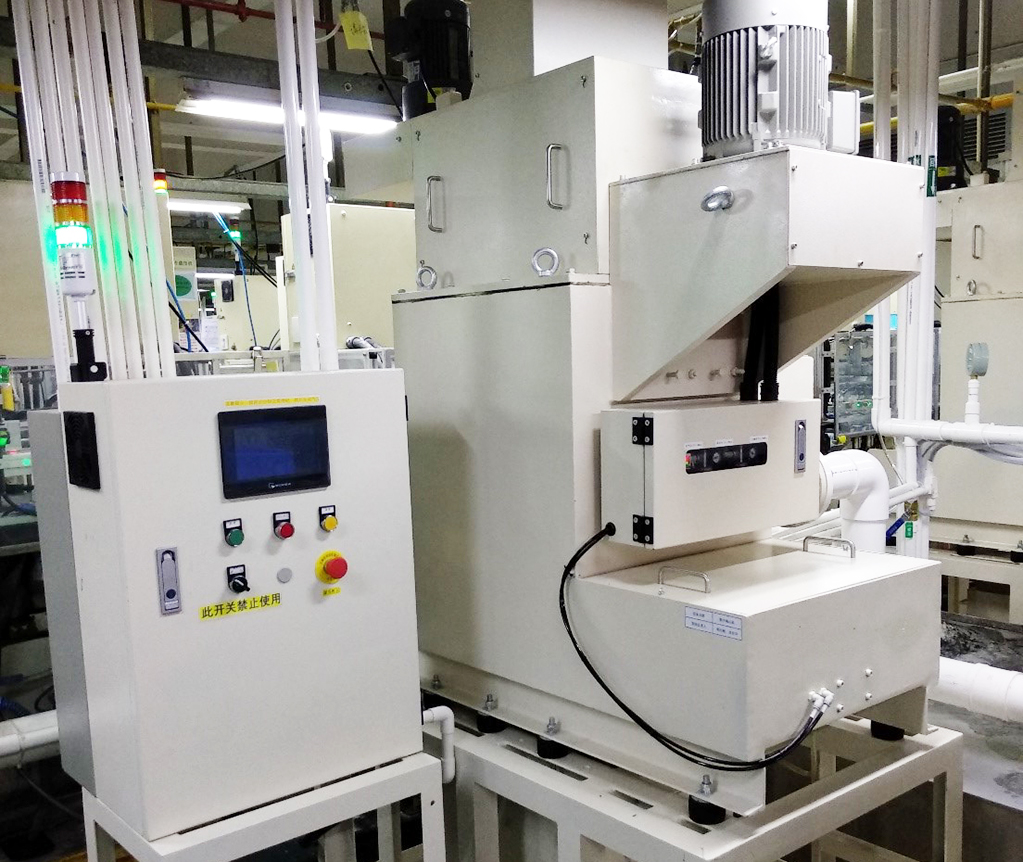
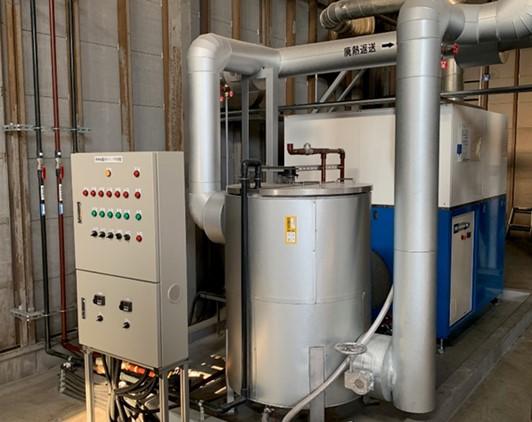
Reduction of industrial waste by volume reduction of grinding waste liquid
The Kagoshima Kokubu Plant implemented forced air evaporators to evaporate water content from polishing waste liquid, which leads to the reduction of waste liquids and the overall reduction of industrial waste. The plant uses waste heat to increase the temperature of the forced air evaporators.
Total Waste Reduction: 458 t/year*
Total amount of reduction by 2 units is shown. (1 unit was implemented in FY2023).

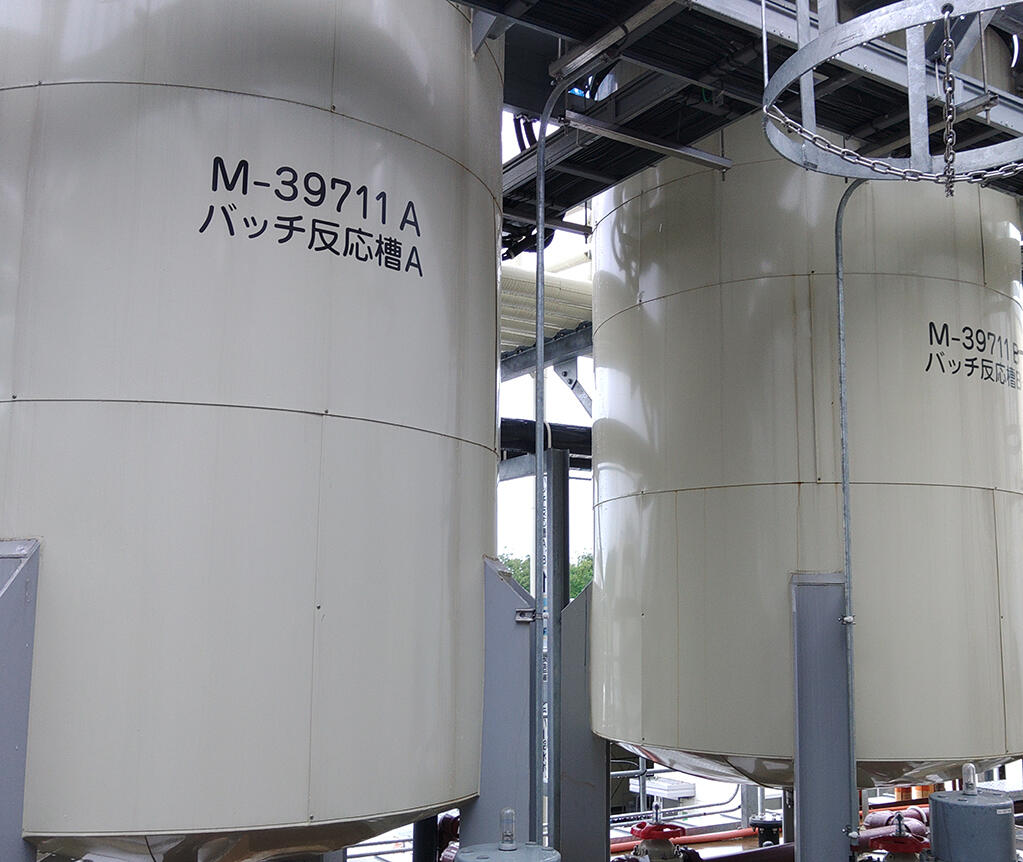
Reduction of Industrial Waste by Implementation of Fenton Pre-treatment Equipment
The Kyoto Ayabe Plant implemented Fenton pre-treatment equipment to process wastewater containing high-concentrations of organic substances. Before implementation, the plant was unable to process concentrated wastewater using previous water treatment methods, forcing disposal as industrial waste. Implementation of the Fenton pre-treatment equipment allows the plant to process concentrated wastewater using currently available methods, which reduces the discharge of industrial waste.
Total Waste Reduction: 676 t/year

Reduction of industrial waste by volume reduction of grinding waste liquid
KYOCERA OPTEC (DONGGUAN) CO., LTD. reduced its industrial waste by installing centrifuges for its lens manufacturing process, which allow polishing solution to be reused by separating out impurities.
Total Waste Reduction: 120 t/year
