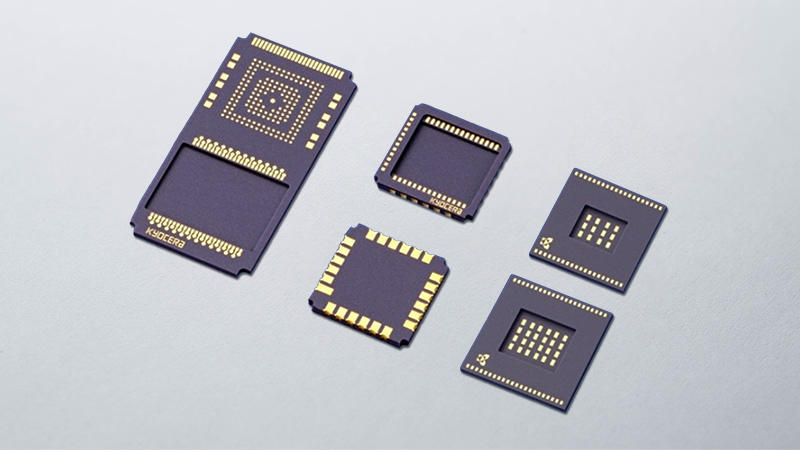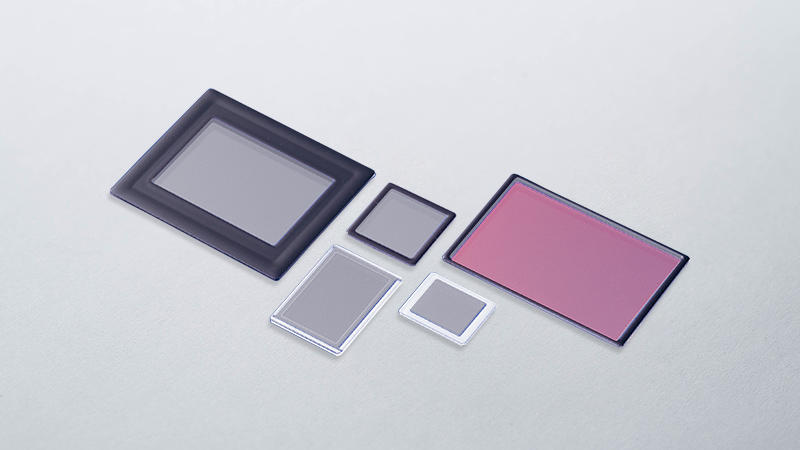
Ceramic Packages / Lids for Imaging Sensor
Kyocera offers ceramic packages and optically coated matching window lids for CCD/CMOS image sensors.
Features
We offer matching window lids for any package; our one-stop service can reduce your design time. Please contact us for a consultation.
What are CCD and CMOS Image Sensors?
An CCD or CMOS image sensor is a semiconductor that converts light from a camera lens into electrical signals. The image sensor is often referred to as an ‘electronic eye’ because it functions like the human retina.
Example of CCD/CMOS Image Sensor Structure and Mechanism
Structure
CCD and CMOS image sensors aggregate many photodetectors and are composed of three layers: microlenses; color filters; and photodiodes, as shown below. (Example of CMOS Image Sensor Structure)
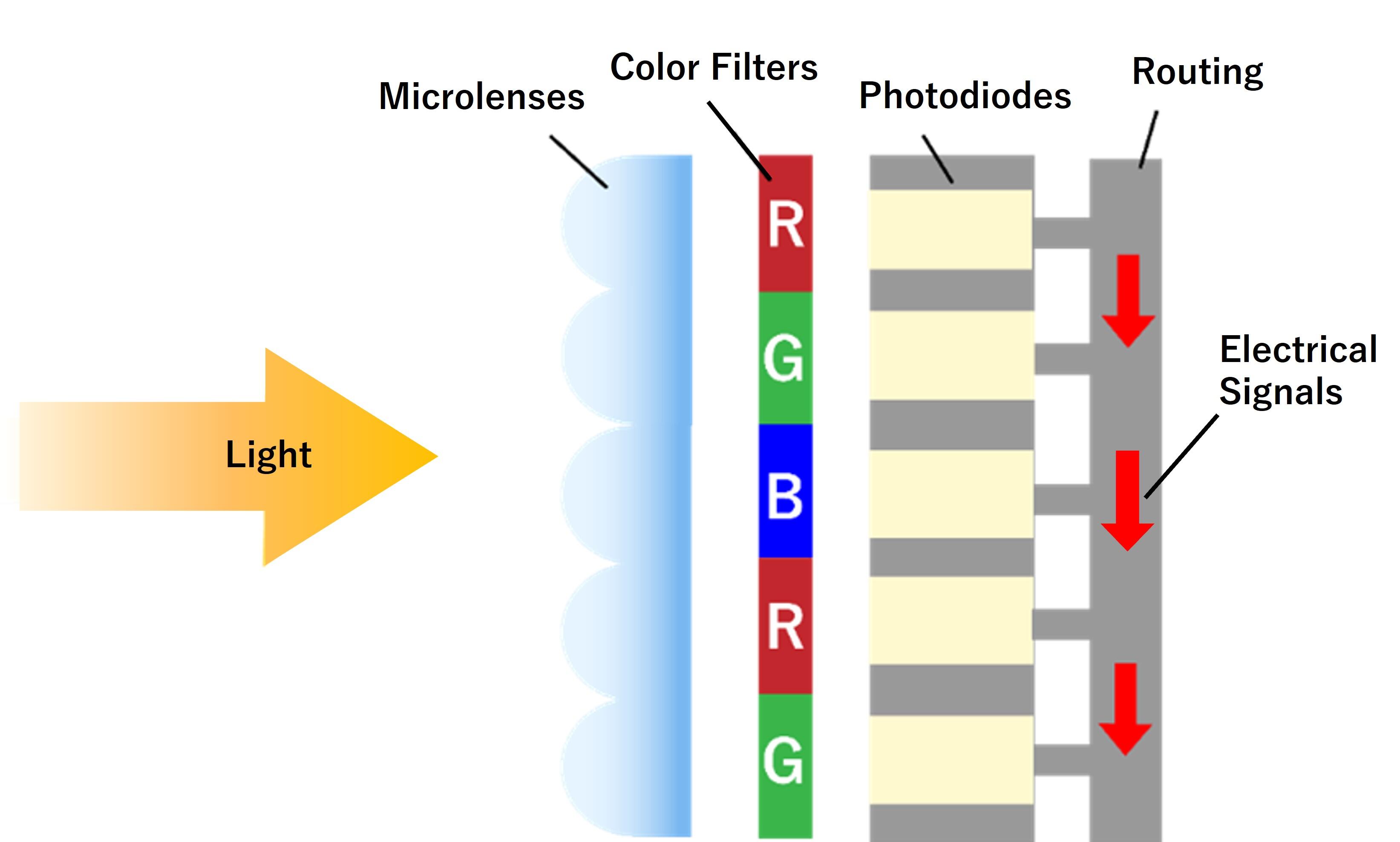
Mechanism
Light passing through a microlens is converted into an electrical charge after passing through a color filter, where the light is separated into different colors, and then through a photodiode.
Visible Light Image Sensors
Visible light image sensors can be broadly classified into two categories: CCD and CMOS image sensors, which differ in terms of their manufacturing processes, and digital signal processing methods.
Differences Between CCD and CMOS Image Sensors
CCD (Charge Coupled Device) image sensors use photodiodes to convert photons into electrical charges. These charges pass between neighboring elements like bucket relays, are converted into signals, and then transferred to one amplifier.
CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) image sensors differ from CCDs in that each pixel in the device has its own amplifier. Light converted into a charge by each photodiode is then converted into a signal and transferred to its own amplifier through ON/OFF switching.
CCD vs. CMOS Image Sensors: Advantages and Disadvantages
While CCD image sensors transfer the charge from a bucket relay system and convert it into one signal at the device level, CMOS image sensors convert charges into signals at the pixel level. This makes it possible to read many sensor pixels simultaneously, which reduces power consumption and speeds up the transfer process.

CCD, the older technology, was the mainstay of the first digital cameras and other imaging products, including telescopes. More recently, the rapid spread of smartphones and other mobile devices has accelerated the technological development of CMOS image sensors, which continue to improve in price, power consumption, and processing speed. Consequently, CMOS image sensors have become a mainstream solution.
Image Sensor Applications