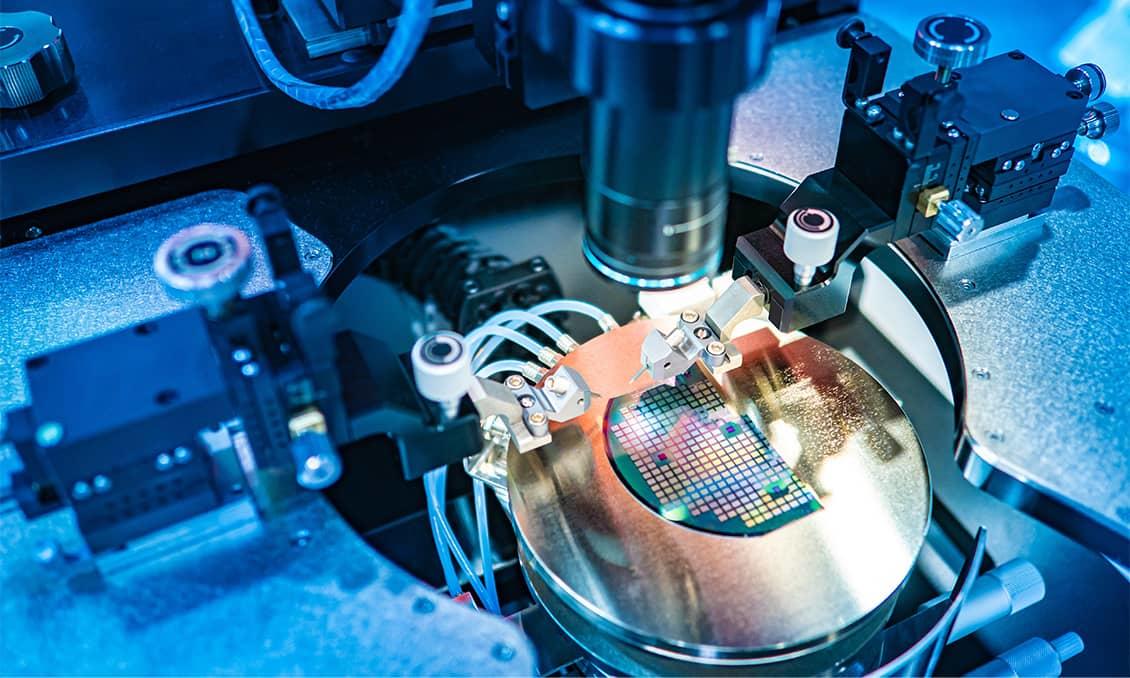
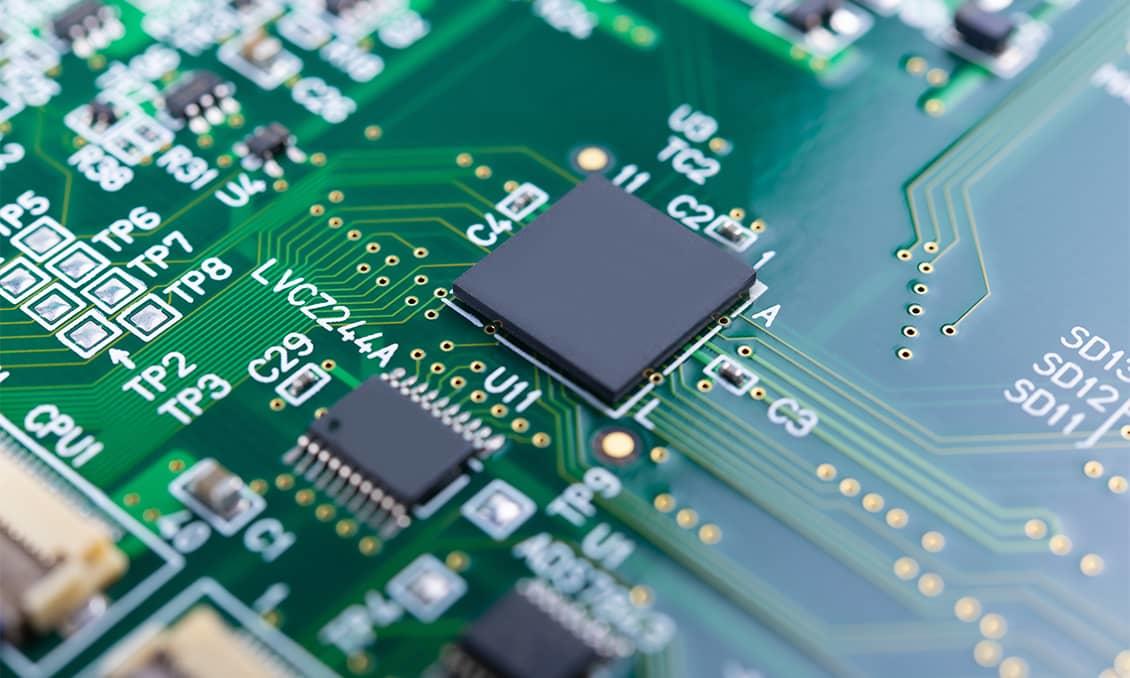
Ceramic Properties
Thermal Properties
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
The ratio that a material expands in accordance with changes in temperature is called the coefficient of thermal expansion. Because Fine Ceramics possess low coefficients of thermal expansion, their distortion values, with respect to changes in temperature, are low. The coefficients of thermal expansion depend on the bond strength between the atoms that make up the materials. Covalent materials such as diamond, silicon carbide and silicon nitride have strong bonds between atoms, resulting in low coefficients of thermal expansion. In contrast, materials such as stainless steel possess weaker bonds between atoms, resulting in much higher coefficients of thermal expansion in comparison with Fine Ceramics.
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (40 - 400℃) × 10-6/K |
Material Name & Code | Features | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Small
Large
|
<|0.05|(23℃) 1.5 (40 - 400℃) |
Cordierite2MgO·2Al2O3·5SiO2
CO220O
|
This material has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion and has a small size change due to temperature change. |
| 2.8 | Silicon NitrideSi3N4
SN240O
|
This material has excellent heat shock resistance and wear resistance, and has high strength even at high temperatures. | |
| 3.7 | Silicon CarbideSiC
SC1000
|
Lightweight, highly corrosion-resistant and excellent heat-resistant material. | |
| 4.6 | Aluminum NitrideAlN
AN216A
|
It's a material with high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation. | |
| 7.2 | AluminaAl2O3
AO479O(99%Alumina)
|
It is a widely used material with high electrical insulation and mechanical strength. | |
| 7.2 | YttriaY2O3
YO100A
|
This material has excellent corrosion resistance in a plasma environment. | |
| 7.6 | CermetTiC,TiN
TC030O
|
It is a composite material of TiC or TiN and metal, and has excellent strength and wear resistance. | |
| 7.7
parallel to c-axis
|
SapphireAl2O3
SA100
|
It's a single crystal of alumina, a transparent material. | |
| 7.7 |
SteatiteMgO·SiO2
SO210O
|
This material has excellent electrical and mechanical characteristics. | |
| 9.7 |
Forsterite2MgO·SiO2
F1120O
|
Smooth surface and excellent insulation at high temperature. | |
| 10.5 | ZirconiaZrO2
ZO201N
|
It is a material with high strength and fracture toughness. | |