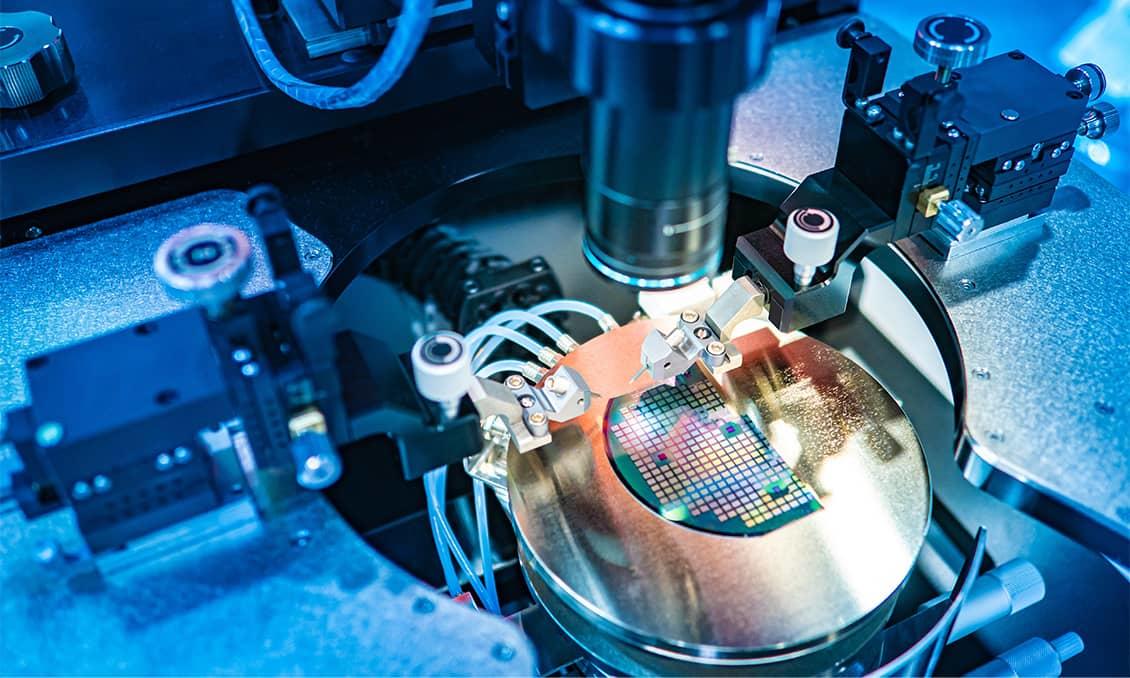
Were you aware of the vacuum components?
Kyocera's ultra-high vacuum metallized components are utilized in sealed containers (chambers) for manufacturing and scientific experimentation in different environments, such as vacuum, liquid, and gas environments.
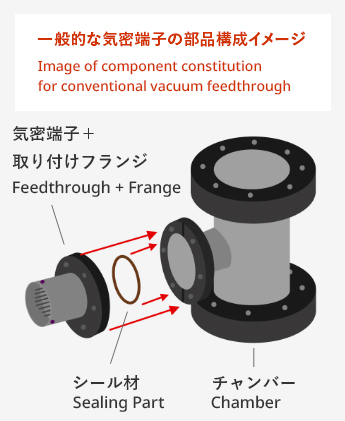
These components generally have a structure that is hermetically sealed between the conductive portion and the insulating portion. Kyocera uses fine ceramics for the insulating portion. The vacuum component is welded to the flange and installed in a chamber using an O ring and a gasket to secure hermeticity.
Product Types
| Types | Description |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Feedthroughs | Also called hermetic seals, feedthroughs, or vacuum current feedthroughs. Attached to sealed containers for taking in and putting out signals or current/voltage. |
| Electrical Insulator Parts | Used for electrical insulation of piping connections. |
| Sapphire Windows | Optical windows featuring single-crystal sapphire to observe the inside of the chamber. |
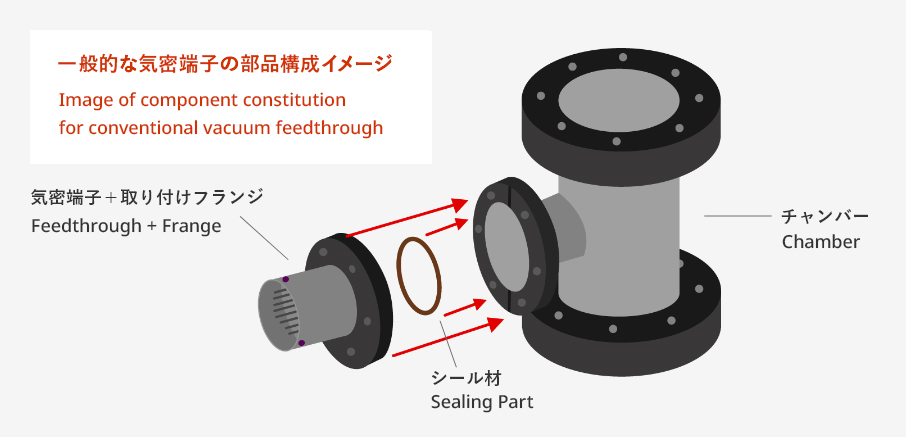
Ceramic-to-Metal Bonding Technology
Kyocera utilizes metallization and brazing for bonding ceramic and metallic members to manufacture ultra-high vacuum components.
Ceramic and metal parts are joined by metallization and brazing.
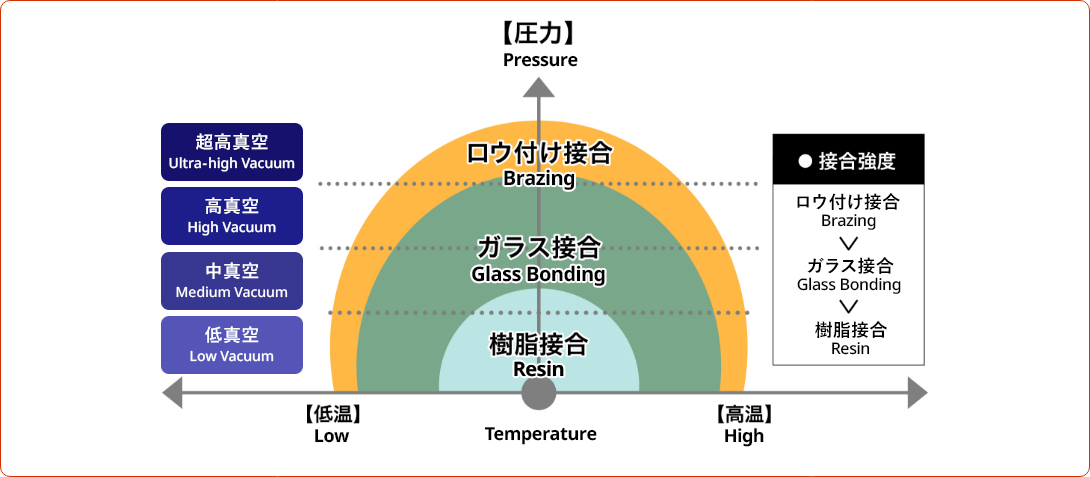
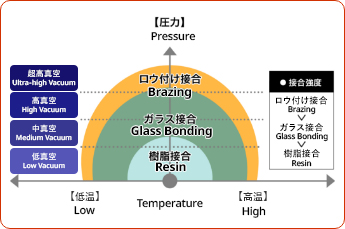
Generally, ceramic-to-metal bonding technology is divided into the following types: bonding with resin, bonding with glass, and bonding with brazing.
resin bonding
Components using resin bonding cannot be used in ultra-high vacuum environments because the vacuum will not increase due to outgas from the resin.
Glass bonding
Glass bonding cannot maintain hermeticity due to insufficient bonding strength in ultra-high vacuum environments, although it can prevent outgas generation.
In contrast, bonding by metallization and brazing enables high hermeticity and bonding strength, even in the harsh environment of an ultra-high vacuum.
By integrating the fine ceramic manufacturing and metallization technologies that have been cultivated for many years, Kyocera's ultra-high vacuum components are produced and inspected in accordance with strict standards. Applications are expanding into areas requiring precise reliability, such as space development.
Scope of application by joining method (conceptual diagram)
Ceramic to Metal Assemblies
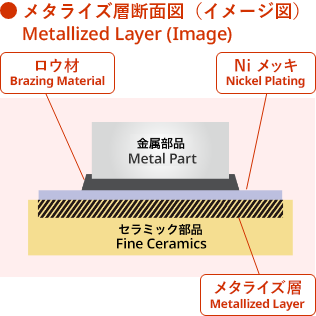
Strength and Hermeticity Achieved by Metallization and Brazing Bonding Technology
Bonding with brazing is essential for achieving ceramic-to-metal bonding with high strength and high hermeticity. However, the direct bonding of ceramics with metal generally results in poor characteristics leading to an inability to use the resulting products due to the weak strength. We therefore utilize metallization and brazing bonding technology, which first creates a metal layer on the ceramic surface (metallization) and then brazes the metal on the metallic surface to achieve ceramic-to-metal bonding with high strength and hermeticity.
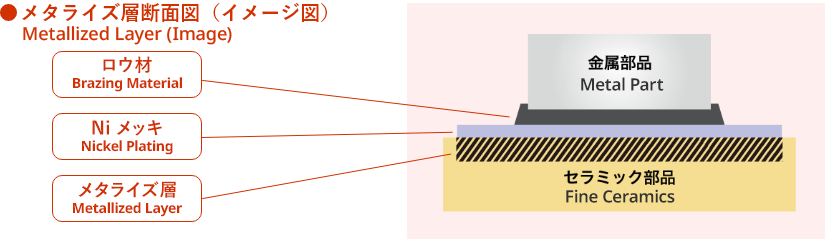
Metallization Process
-
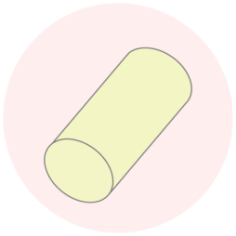
Fine Ceramics Part
Making high-precision ceramic components by means of fine ceramic manufacturing technologies with a long history of cultivation.
-
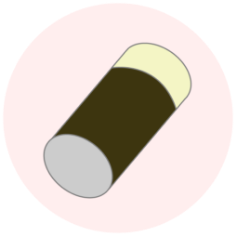
Forming Metallized Layer
Forming a metallized layer for bonding ceramics to the metal.
-
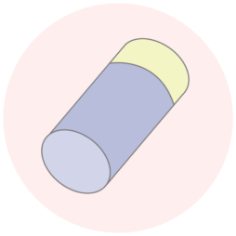
Nickel Plating
Nickel plating to protect the metallized layer and support the flowability of brazing material
-
Brazing
Bonding a metal part to a ceramic part with a metallized layer by brazing.
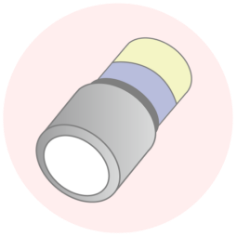
-
Welding
Welding a metal part to another part such as a flange.
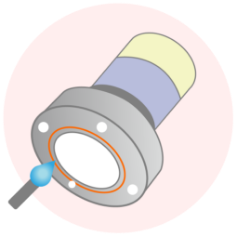
-
Helium Leak Test
Every finished product is subject to a helium leak test to ensure hermeticity. Check whether airtightness is ensured.
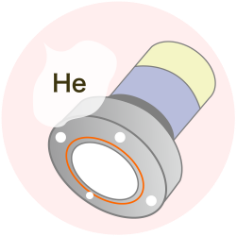
Index of Catalog
The catalog introduces the following material properties and product examples. Download the PDF to learn more.
-
Were you aware of the vacuum components?
-
Ceramic to Metal Assemblies
-
Ordering Process
-
For Product Selection
Circular Multi-Pin Feedthroughs / Coaxial Connectors / Feedthroughs / Isolators / Sapphire Windows / Introducing New Technology
-
Custom-designed Ceramic Chambers
-
Technical Information
Characteristics of Ceramics / Precision Shaping and Matching / Material Comparison Chart / Characteristics of Metals (Example) / Metallization Technologies and Materials / Basic Design of Ceramic-to-Metal Bonding