Kyoto Sangyo University established the Koyama Astronomical Observatory in 2010. Based on the concept of "industry-academia collaboration," which is also the university's spiritual pillar, the observatory has been developing cutting-edge astronomical instruments as a "monozukuri" (manufacturing) base, with a focus on collaboration with various companies. Particularly in the development of infrared astronomical instruments, the observatory has led the world in observational research using the high-sensitivity near-infrared high-dispersion spectrograph "WINERED". It is also developing small and lightweight infrared high-dispersion spectrographs that can be mounted on ultra-small satellites.
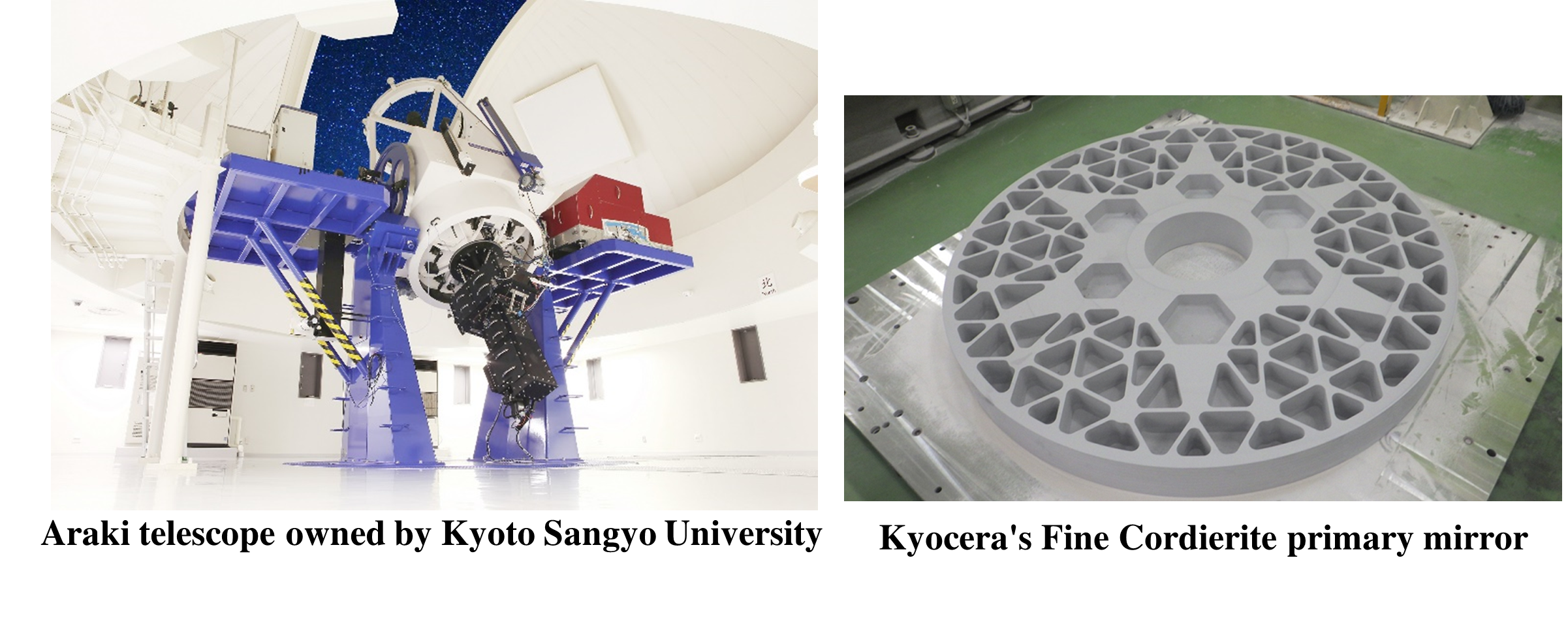
To realize a reflecting telescope equipped with a large, lightweight fine cordierite mirror, a world's first achievement*1, and to develop ceramic reflective optical systems for infrared astronomical observation instruments, Kyoto Sangyo University, Kyocera Corporation (hereafter "Kyocera"), and Photocross, Co., Ltd. (hereafter "Photocross") have reached a comprehensive and detailed agreement. This agreement outlines each party's roles and responsibilities, the project timeline, and the expected outcomes, ensuring a coordinated and effective collaboration.
*1 As of July 31, 2024, this is the first time a primary and secondary mirror made of cordierite will be installed in a large ground-based telescope (according to Kyocera's research).
For more information, please see:
https://global.kyocera.com/newsroom/news/2024/000941.html