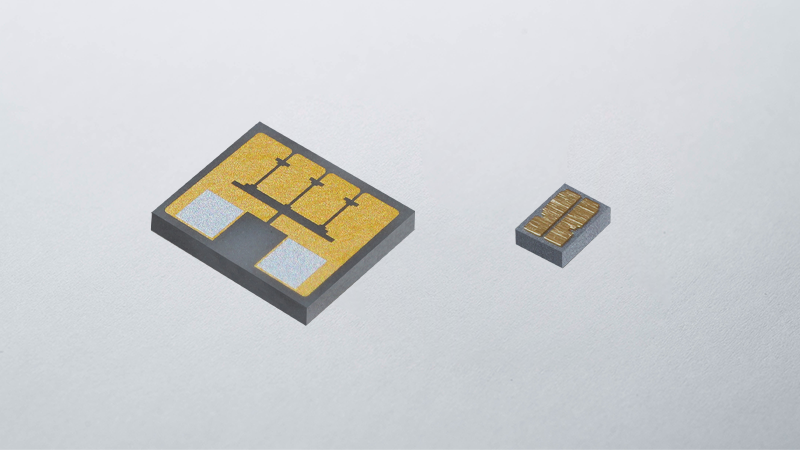
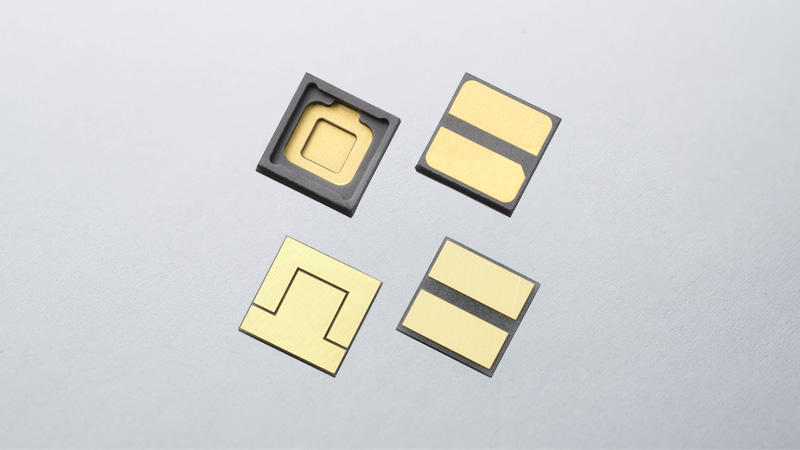
What Are Thin-Film Circuit Boards?
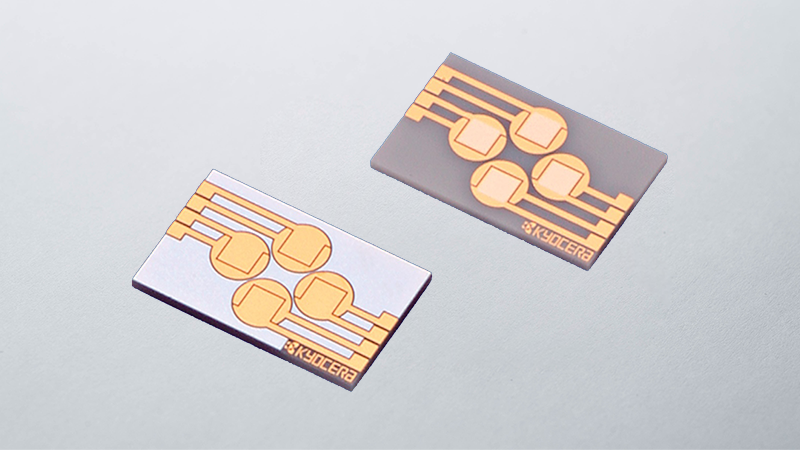
As the name suggests, "thin films" are very thin layers of materials deposited and plated onto the surface of a substrate. Thin-film circuit boards are manufactured using vacuum deposition technology to form thin-film conductive and insulating layers on the surface of the substrate, which is typically made of ceramic, glass, metal, resin, or other materials. In general, thin-film circuit boards are used where high-precision electronic circuitry is required.
Learn more about Kyocera's thin-film technology.
Click here for Kyocera's thin-film circuit board manufacturing process.
Kyocera's film deposition process is outlined here.
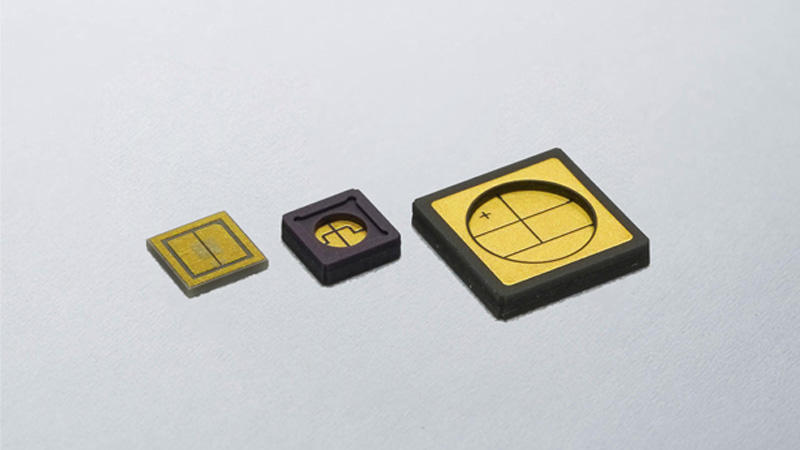
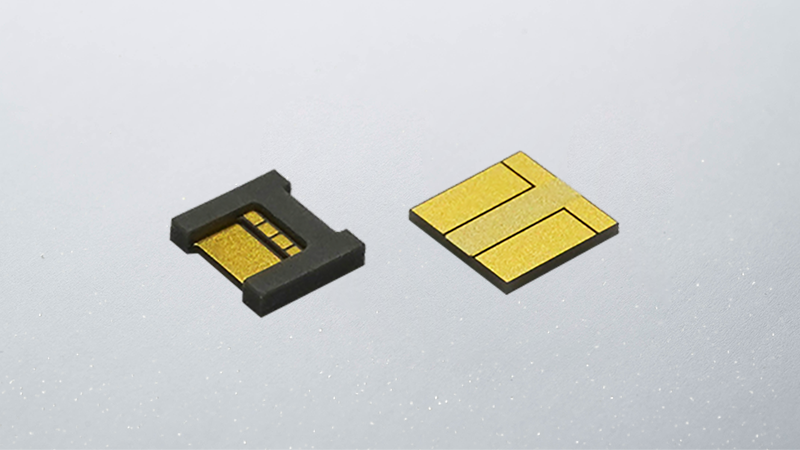
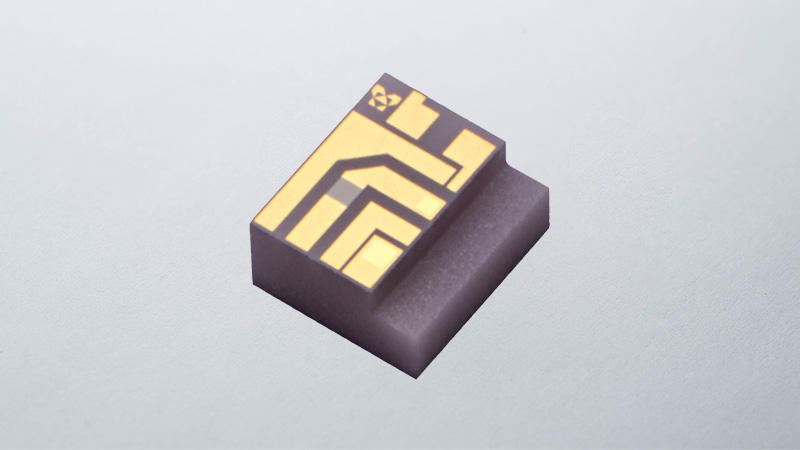
Kyocera's Ceramic Thin-Film Circuit Boards
Overview
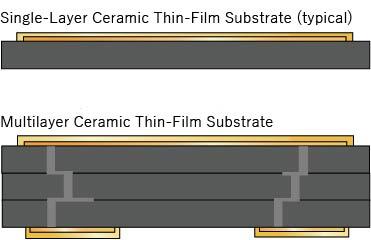
In general, ceramic thin-film circuit boards often employ solid, single-layer ceramic as a substrate material, which becomes a single-layer ceramic thin-film substrate. Kyocera offers multilayer ceramic thin-film substrates as well, which can achieve higher electrical routing density. In addition, Kyocera can propose custom designs to meet specific customer requirements, including external processing to add holes, steps, and/or grooves; applying AuSn deposition on chip mounting areas; depositing resistor patterns; and plating thicker metal patterns for high-current applications. Click below for more information.
Applications for Ceramic Thin-Film Circuit Boards
Ceramic thin-film circuit boards are used for devices requiring high-precision circuitry and higher thermal dissipation, including automotive applications requiring high reliability.
Typical Applications
Thin-Film Processing Methods
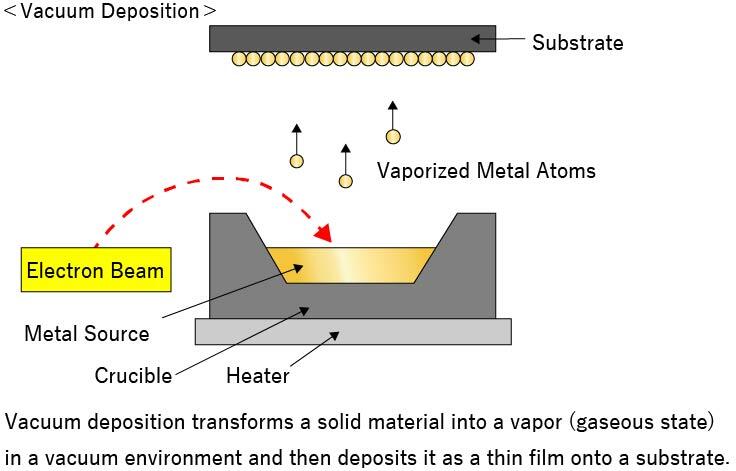
1. Vacuum Deposition
Vacuum deposition is a technique in which vaporized metal atoms are deposited onto a substrate or other surface in a vacuum. This method produces uniform film thickness.
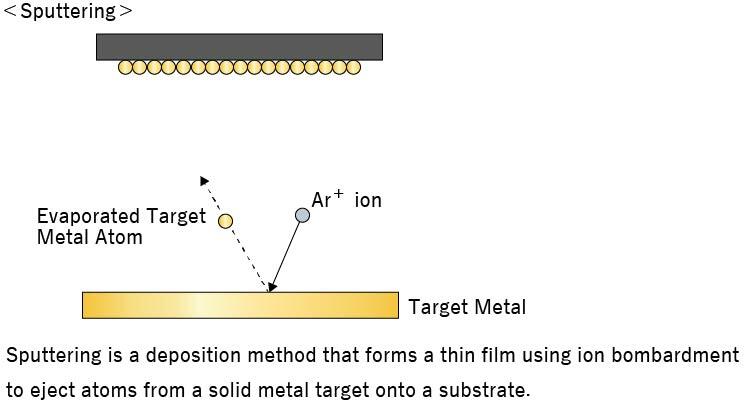
2. Sputtering
Sputtering is a technology to deposit evaporated metal atoms from a target metal onto a substrate surface, allowing the formation of a thin, uniform layer over a large area. In addition, since this process allows continuous processing, it is suitable for products that are mass-produced at low cost.