Ceramic Package Technology:
Supporting XR Device Evolution

XR Technology is Rapidly Evolving
Extended Reality (XR) is a rapidly evolving, cutting-edge technology that merges the physical and virtual worlds into an immersive, interactive, real-time user experience. Kyocera's ceramic packages have a proven track record in enabling critical levels of performance from sensors and other devices essential to XR technology. Kyocera also provides development support for creating high-performance modules by integrating multiple devices into a single, miniaturized package.
What Is XR ?
XR (Extended Reality) is the collective term for VR (Virtual Reality), MR (Mixed Reality), and AR (Augmented Reality). It is a revolutionary set of technologies that create immersive, simulated experiences by engaging the senses, leading the brain to perceive a highly realistic virtual or augmented world. This innovative approach transcends the boundaries between the virtual and the real, creating a sense of immersion in the Metaverse(*) with a richness of experience that unlocks profound possibilities for the future.
- ※What Is Metaverse ?
-
The Metaverse is a three-dimensional virtual space on the internet, named by combining "Meta" (meaning "transcendence") and "Universe" (a reference to everything in the cosmos). In the Metaverse, users become avatars who freely interact with other avatars, buying and selling goods, conducting and participating in events, learning, experiencing, simulating, and engaging in a wide range of real-life and imaginary activities.
Global VR headset shipments are expected to continue to increase with XR technology adoption worldwide.
Devices Used for XR
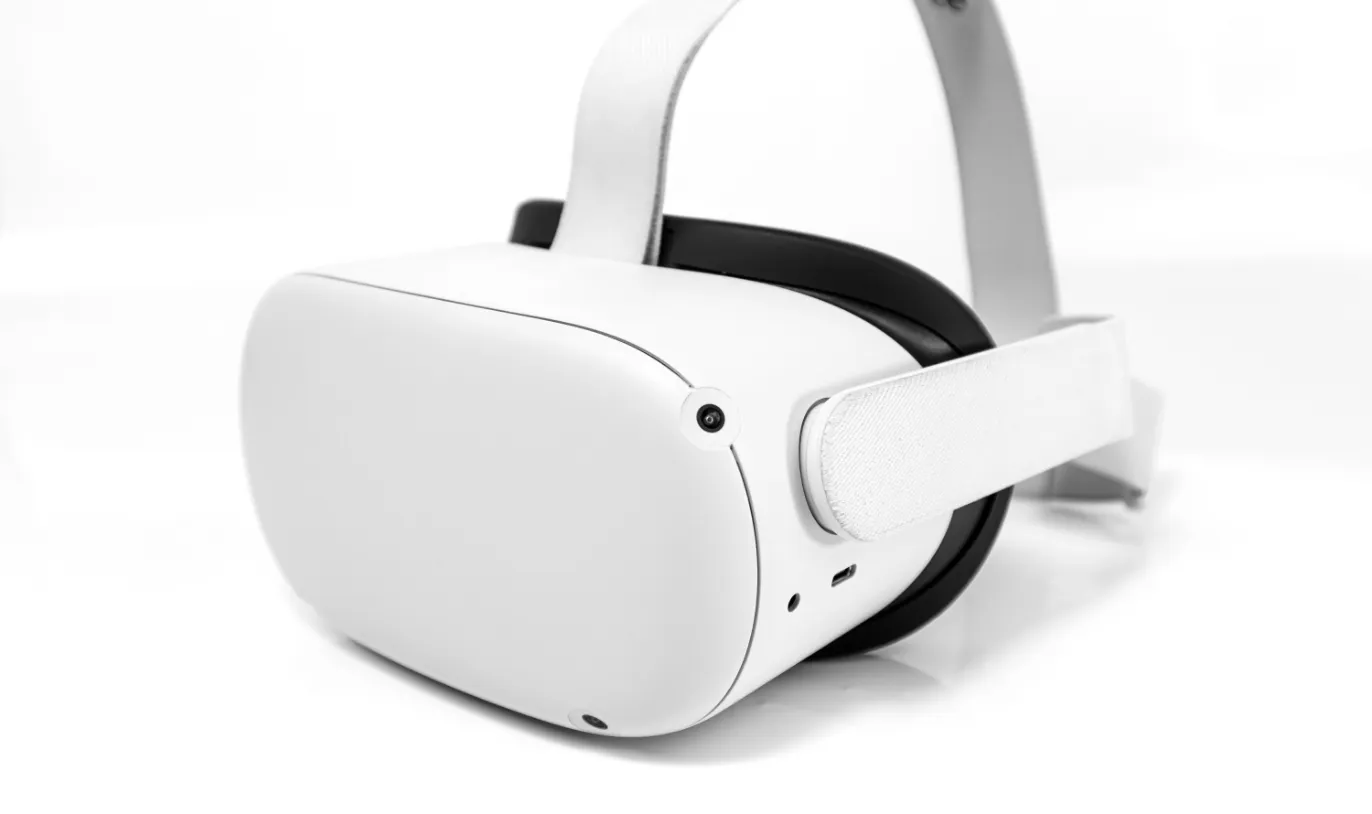

Head Mounted Display
(HMD)
A video display worn on the head, mainly for VR.
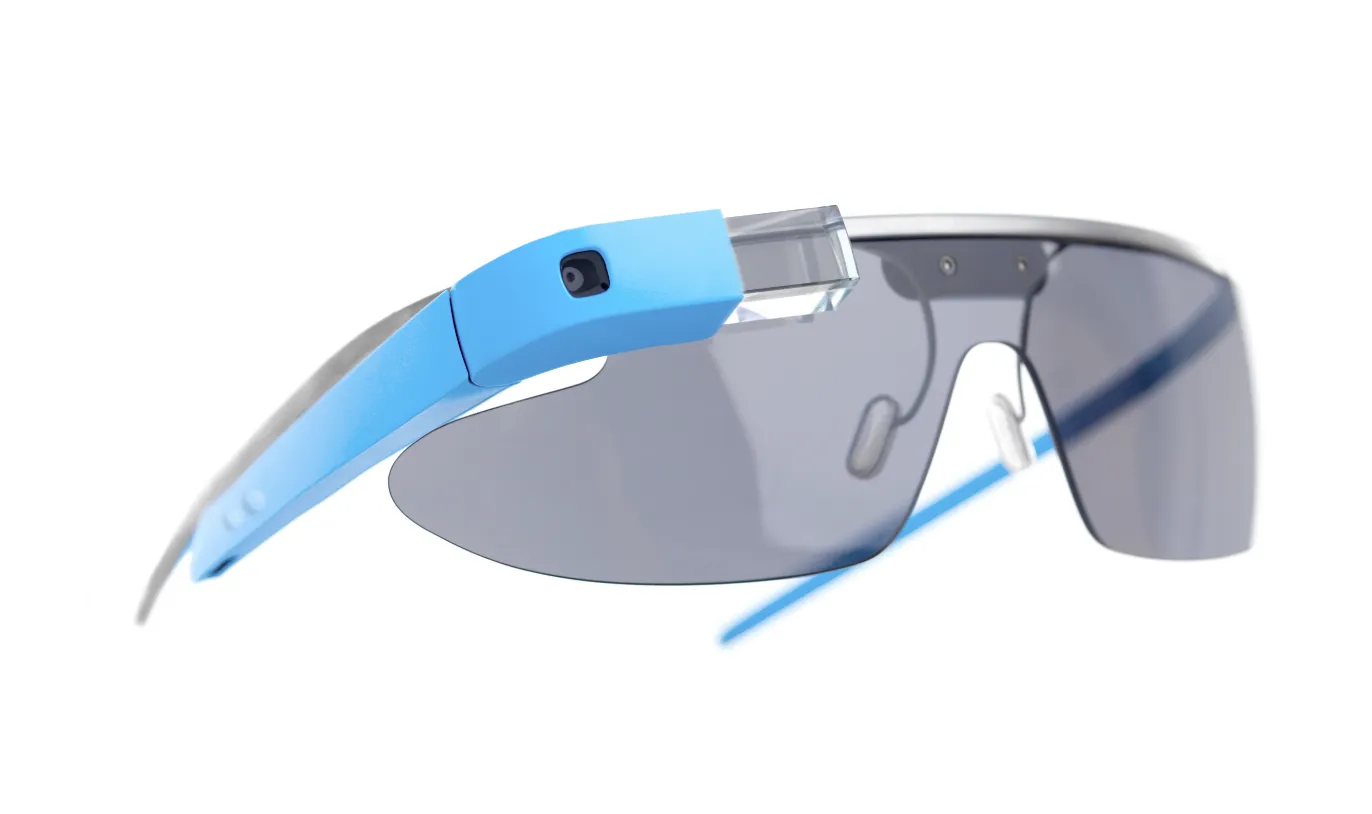
Smart Glasses
Eyeglass-shaped wearable devices with displays mounted on the lenses, primarily for AR, where virtual information is superimposed over real scenes.

Key Devices
Used in XR Equipment
XR hardware is equipped with numerous devices, including light sources for depicting images and sensors for detecting objects. Some key examples are shown here.
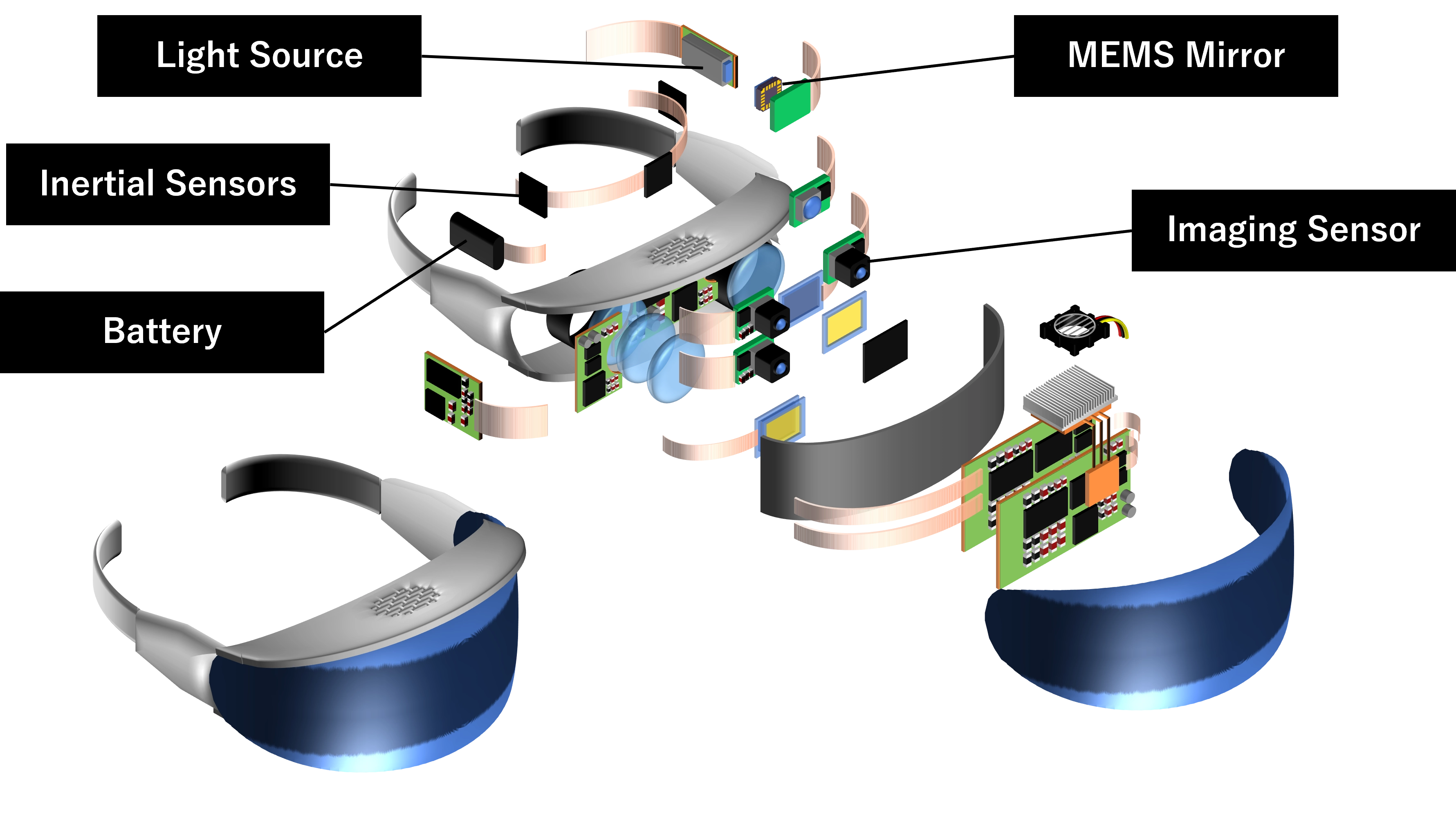
| Key Devices | Imaging Sensor | Inertial Sensor | Light Source | MEMS Mirror | Battery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device Function |
Perceive surroundings | Perceive surroundings | Image depiction / understand your surroundings | Image depiction | Power storage for device operation |
| Function Details |
Sensor converts light into electrical signals; indispensable for XR instruments, including smart glasses. | Examples: accelerometer, angular rate sensor. Accelerometer detects changes in velocity, while angular rate sensor detect the angle of rotational motion. | A device that emits light to depict images or to gain information about real surroundings. | A "moving mirror" that uses MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology. A tri-color RGB laser projects light onto a high-speed, computer-controlled MEMS mirrors to depict images. | A device that stores electricity to power the hardware. |
Characteristics of Each Key Device
The features of ceramic packages can help solve performance challenges associated with each key device, as shown in the chart below. Ceramic packages can also resolve challenges relating to miniaturization and functionality by allowing many individual devices to be integrated into a single, compact, high-performance module.
| Key Device | Imaging Sensor | Inertial Sensor | Light Source | MEMS Mirror | Battery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device Requirements |
High Resolution | Small Size Environment-friendly |
High brightness | High resolution Low power consumption |
Environment-friendly |
| Device Challenges |
|
|
|
|
|
| Features of Ceramic Packages |
|
|
|
|
|
| Related Pages |
- ※System Integration
-
Ceramic packages offer a wide range of structual design options, and multiple devices can be integrated into a single package for system integration.
Example of System Integration Modules
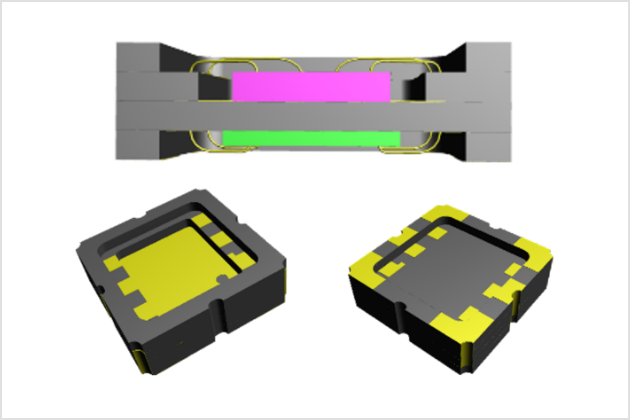
Cavities (both front and back) 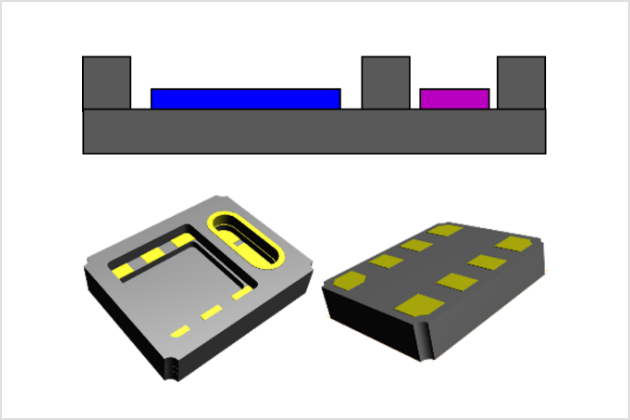
Dual cavity (one side)
Ceramic Package Solutions for XR
Kyocera's ceramic packages enhance performance in a variety of devices, including semiconductors and sensors, and Kyocera is leveraging its expertise to achieve new levels of miniaturization and system integration. By driving the miniaturization and lightweighting of increasingly advanced hardware, Kyocera will continue to support the XR evolution.
We look forward to offering solutions for your new XR devices.
Please feel free to contact us