Challenge: Protecting Devices from the External Environment
To ensure the reliable performance of semiconductors and electronic components, packaging must provide effective protection against moisture and dust. Hermetic sealing is one of the most effective methods of providing this protection. The material properties of ceramic packages and sealing methods that enable hermetic sealing are outlined below.
Ceramic Packages for Hermetic Sealing
Ceramics provide more effective hermetic sealing than other materials, offering package hermeticity levels up to 1.0 x 10-9Pa*m3/s.
*Note: Some materials or structures may present unique hermeticity challenges.
Click here for details of leak testing (a test to confirm hermeticity).
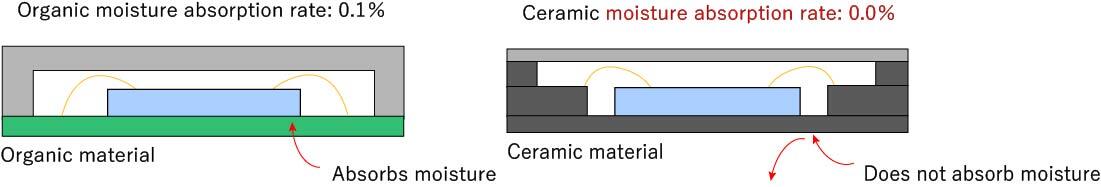
Ceramics Do Not Absorb Moisture
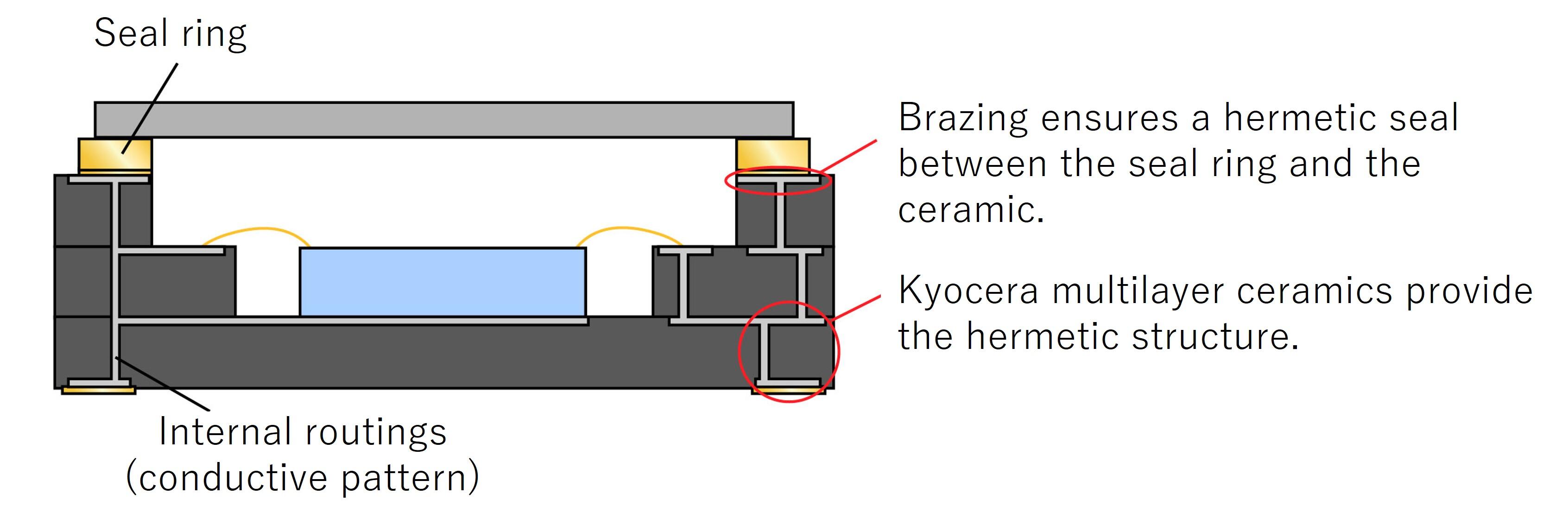
Methods of Hermetic Sealing
Solder sealing (including AuSn) and seam welding are two widely used methods of hermetic sealing.
AuSn Solder Sealing

- Lid material: Metal or ceramic
- Advantages: Lower thermal stress
- Metal lids provide ground-shielding
- Disadvantages: Relatively high sealing temperature (around 320℃)
Seam Welding
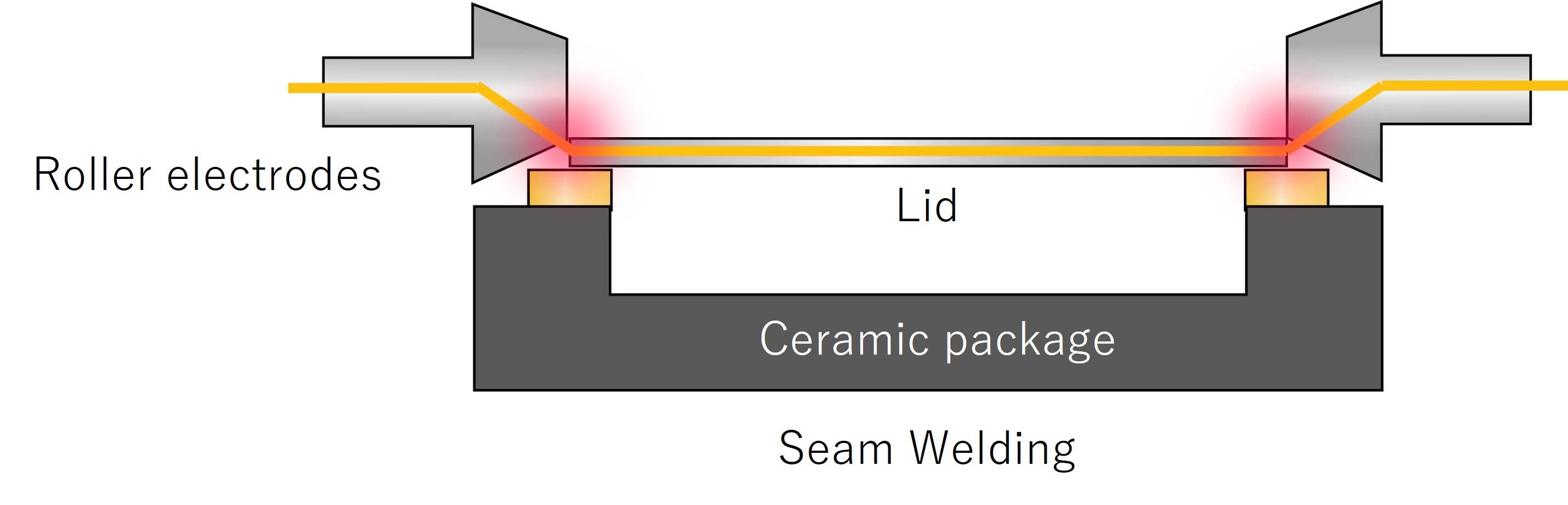
Another sealing method known as "seam welding" involves placing a metal lid on a metal seal ring on the ceramic package and welding the metals using roller electrodes.
- Lid material: Metal
- Advantages: Metal lids provide ground-shielding
- Due to local welding, less thermal load on components;
- can offer electromagnetic shielding
- Disadvantages: Requires a metal seal ring on the package.
*Please click here for other sealing methods.
*Kyocera also provides stress simulation during sealing. For details, click here.