Fine Ceramics, sometimes referred to as "advanced ceramics," are engineered materials that support the development of cutting-edge technology.
Fine Ceramics at Work in the Large Hadron Collider
Providing Support 100-m Underground to Control Protons and Observe Experimental Results
Highly reliable components achieve greater airtightness
Fine Ceramics employed by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)
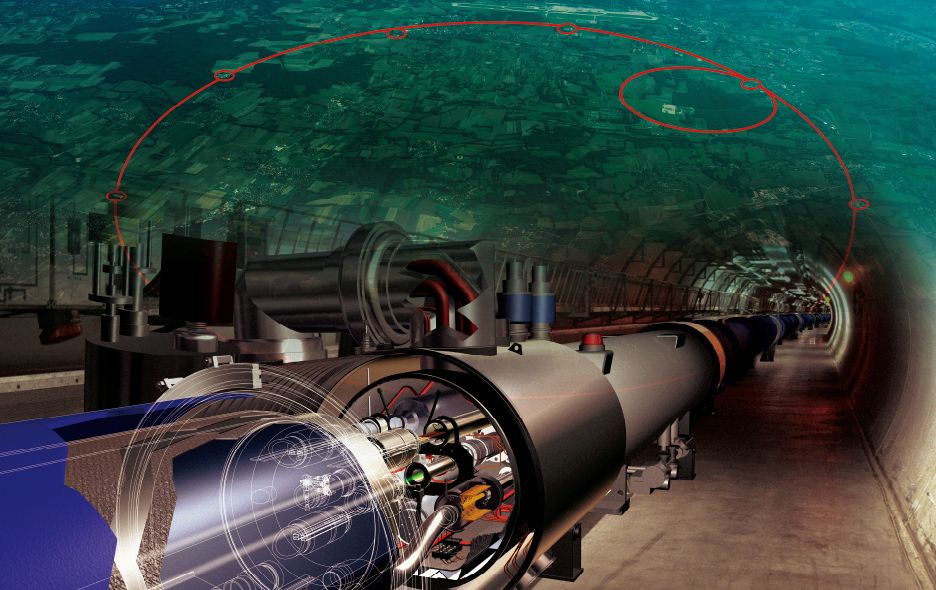

The Large Hadron Collider
(Photo: Courtesy of the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN))
© CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), one of the world's largest research institutes for particle physics, drew global attention with the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012. CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC), which is located in a tunnel 100 m underground with a 27-km circumference , is used for experiments that accelerate protons to almost the speed of light before colliding head-on. Kyocera's Fine Ceramics components play a key role in controlling protons and measuring experimental results due to their superior reliability and unique characteristics that achieve higher levels of airtightness, insulation, and heat resistance.
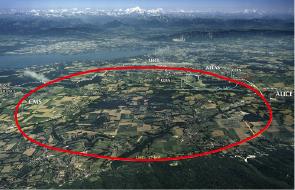
The Large Hadron Collider with a 27-km circumference

Fine Ceramic chamber

Feedthrough
People who read this page also read.

Electricity and Magnetism (1)
Electricity and Magnetism (1)
Electrical Insulation to Inhibit Electricity from Passing Through
Electrical Insulation to Inhibit Electricity from Passing Through
Characteristics of Fine Ceramics

Fine Ceramics in Space
Fine Ceramics in Space
Advancing Space Exploration with Fine Ceramic Technology.
Advancing Space Exploration with Fine Ceramic Technology.
Learning about Fine Ceramics
If you want to use ceramics in business, click here.
Kyocera's Fine Ceramics products (All websites below open in a separate window.)
Product Category
 Semiconductor / LCD Processing Equipment
Semiconductor / LCD Processing Equipment
 Life / Culture / Industrial Machines
Life / Culture / Industrial Machines
 Wireless Communications
Wireless Communications
 Computer Peripherals
Computer Peripherals
 Environmental Preservation / Renewable Energy
Environmental Preservation / Renewable Energy
 Medical Equipment / Devices
Medical Equipment / Devices
 Single-Crystal Sapphire Products
Single-Crystal Sapphire Products
 Metallized / Vacuum Components
Metallized / Vacuum Components
 Electronics Industry
Electronics Industry
 Heaters
Heaters
 Piezoelectric Ceramics
Piezoelectric Ceramics
Search by Material
 Alumina
Alumina
 Silicon Nitride
Silicon Nitride
 Silicon Carbide
Silicon Carbide
 Sapphire
Sapphire
 Zirconia
Zirconia
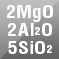 Cordierite
Cordierite
 Yttria
Yttria
 Aluminum Nitride
Aluminum Nitride
 Cermet
Cermet
 Mullite
Mullite
 Steatite
Steatite
 Forsterite
Forsterite
Search by Property/Characteristic


- Thermal Properties
- Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
- Thermal Conductivity
- Heat Shock Resistance

- Electrical Properties
- Insulation / Semiconductivity

- Chemical Properties
- Chemical Resistance






