Challenge: Using High-Temperature Adhesive Materials
Chip/component assembly requires careful attention to adhesive and sealing materials, considering the heat sensitivity of both the chip/component and the package. High temperatures during assembly can deform many conventional package materials. In contrast, ceramic packages withstand higher temperatures and accommodate high-temperature adhesive materials, which expand assembly options and extend reliability. This enhances assembly by avoiding misalignment that occurs when the solder on previously assembled chips/components is remelted. Further, ceramics allow other high-temperature process options, such as baking.
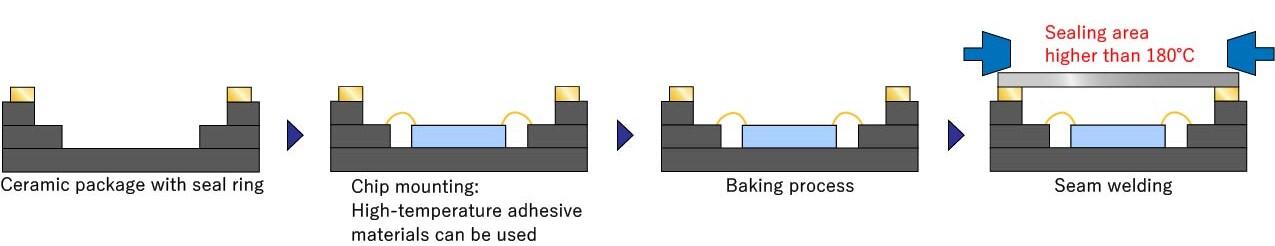
Examples: High-Temperature Die-Attach Processes
Case 1: Misalignment of assembled chips and components can occur during multiple reflow processes.
High-temperature die-attach materials can eliminate this.
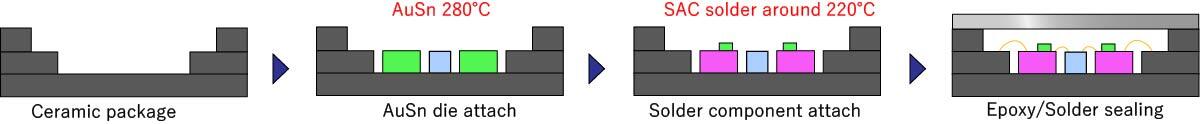
Case 2: Heat during sealing process remelts assembled components and breaks solder joints.
High-temperature die-attach materials can eliminate this risk as well.
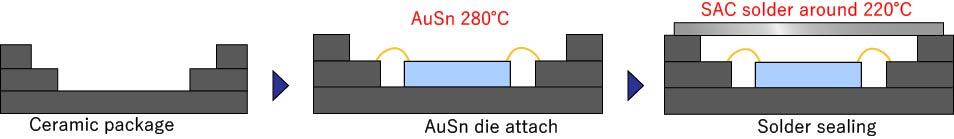
Case 3: A baking process is specified to minimize moisture content before hermetic sealing. Ceramic packages can allow a baking process to be added with no risk of heat deformation during seam welding for hermetic sealing
(*The above case studies are not guaranteed, but are based on comparison with organic substrates; the assembler is responsible for selecting materials, optimizing assembly processes, and managing process variables that collectively enable these results.)

*The melting point of non-metallic (glass) sealing materials changes depending on the type of additives and the composition ratio. For details, please check with the manufacturers of each type of non-metallic sealing material.