Challenge: Dissipating Heat from Microelectronic Devices
Because excess heat impairs performance and can cause device failure, thermal management is a top priority in microelectronic packaging. Kyocera offers a broad line of packaging materials that feature high thermal conductivity, enabling us to match the optimal package material with a customer's performance requirements. Additionally, Kyocera's advanced metallization technology allows us to braze thermally conductive metals, including copper, directly onto a ceramic package. This brazed metal serves as a heat spreader to enhance thermal performance even further.
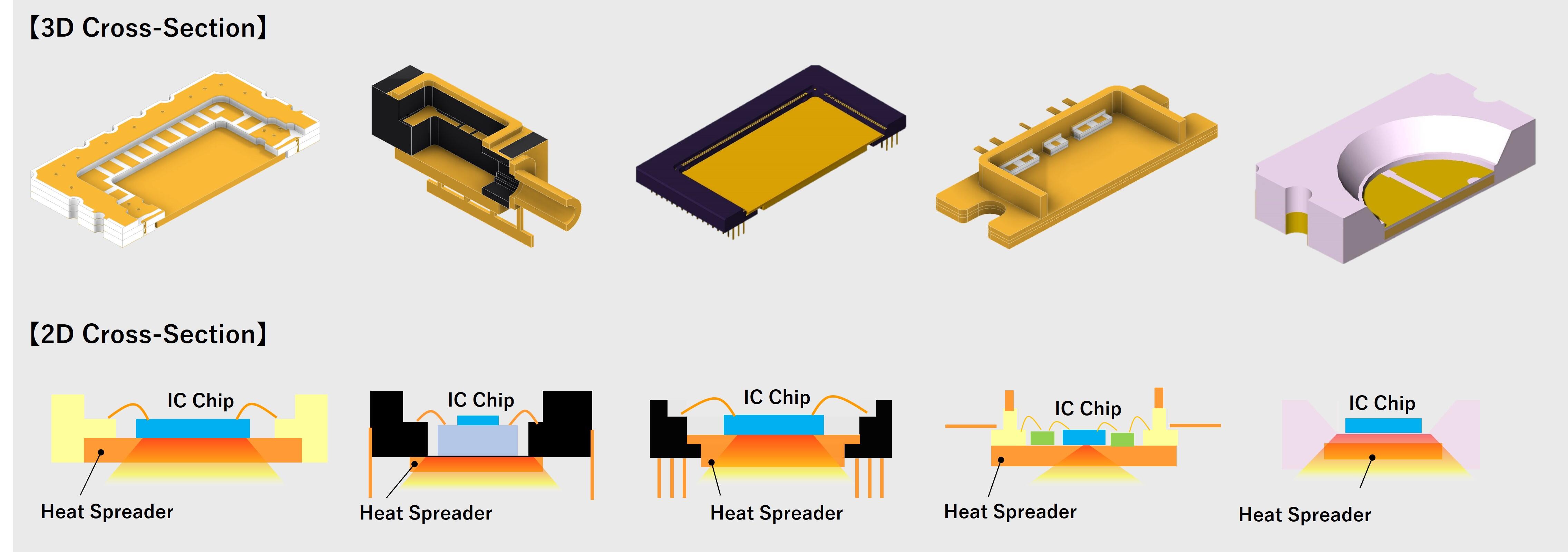
Heat Spreader Design Examples
The illustration below shows examples of ceramic IC packages equipped with heat spreaders. Various other structures are also available; please contact us for details.
Material Properties: Heat-Spreader Metals Commonly Brazed to Ceramics
Kyocera can offer a wide variety of metal heat spreaders, as outlined below. ※O.F.H.C.:Oxygen Free High Conductivity

(**)Thermal resistance is calculated on the following conditions. Material size: 1.0 x 1.0 mm; material thickness: 1.0 mm. Excludes loss factor due to bonding material.
Click here for the simplified thermal resistance formula.
- Values above may vary with material changes or process improvement.
- "CPC" is a registered trademark of A.L.M.T. Corp., identifying a laminated heat dissipation substrate with Cu layers on top and bottom of CuMo compounds.
- "KYCM" and "CM360" are Kyocera’s original material codes.
- "KYCM" is a registered trademark of Kyocera Corporation in Japan and China.
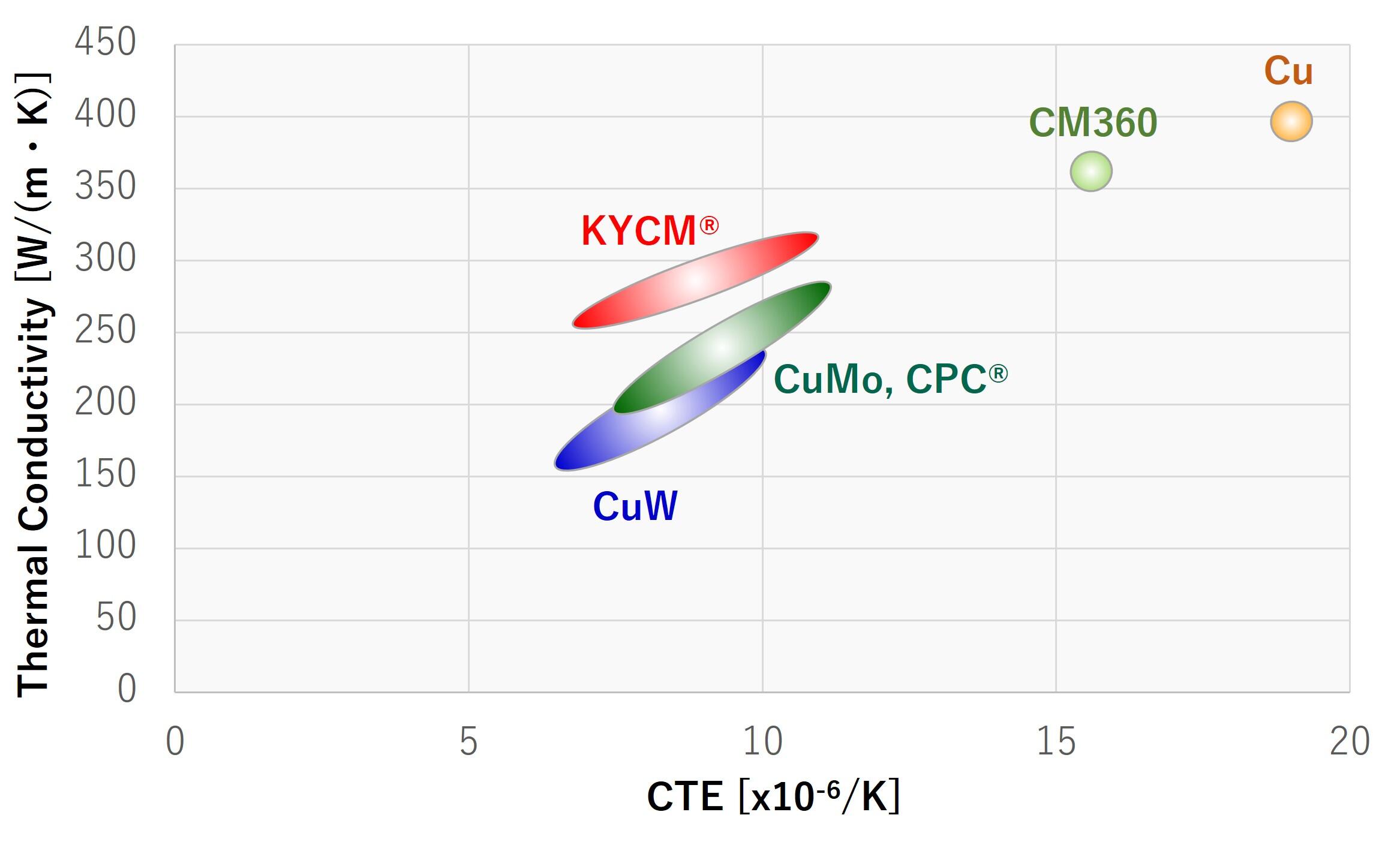
Heat Spreader Characteristics
The chart below shows the relationship between thermal conductivity and CTE for each heat spreader material outlined above.