Kyocera Corporation (Kyoto, Japan; President: Hideo Tanimoto, "Kyocera") today announced that it has developed a Smart-Sensing Research Buoy*1 for continuous ocean data collection, powered by tidal energy harvesting technology from Nagasaki University. A paid trial service for this innovative solution using Kyocera's IoT technology will begin in Japan in April 2025.
As part of this initiative, Kyocera will collaborate with Nitto Seimo Co., Ltd. (President: Hiroaki Kobayashi, "Nitto Seimo") to provide customers a total solution including cloud-based, real-time ocean monitoring, buoy installation, maintenance, and retrieval operations.
*1 Previously referred to as the "Energy Harvesting Smart Buoy"
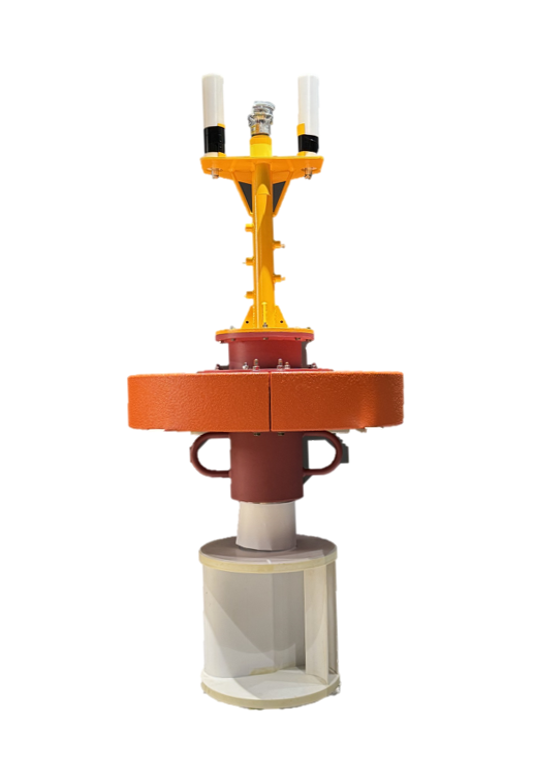 Smart-Sensing Research Buoy
Smart-Sensing Research Buoy
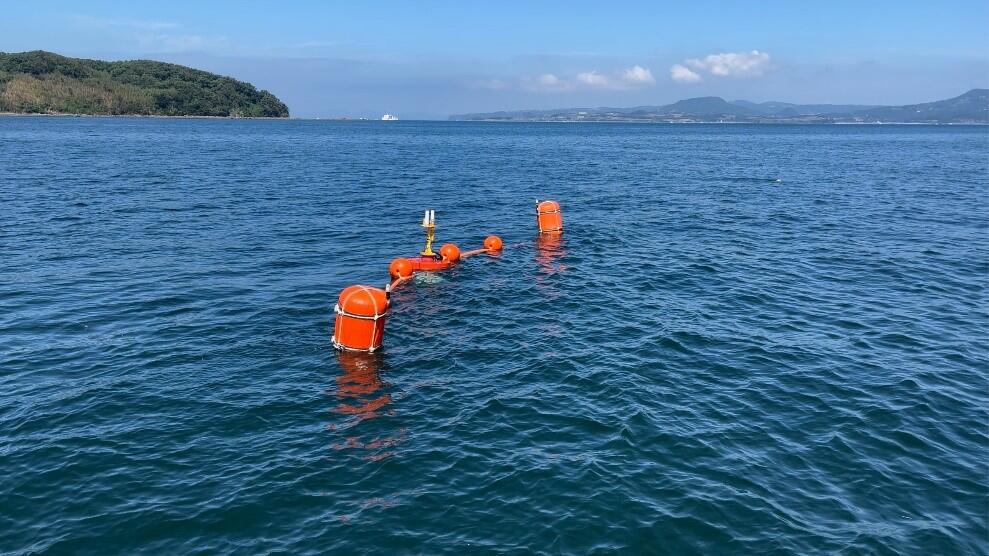

Observation off the coast of Itsuwa Town, Amakusa City, Japan
Development Background:
As climate change and marine resource management become pressing global issues, the importance of accurate and stable ocean data collection is increasing. IoT technology for real-time ocean environment monitoring is expected to revolutionize marine conservation, disaster prevention and sustainable fishing.
However, data collection using research buoys has traditionally faced challenges such as power supply limitations and high maintenance costs, making long-term operation and deployment in remote offshore locations difficult.
Addressing these challenges, Kyocera has developed a Smart-Sensing Research Buoy using tidal current power generation to avoid the need of a conventional power source. This innovative solution, which harnesses ocean currents to generate and store electricity, ensures stable and efficient data collection over the long term, far from power grids, significantly expanding the scope of marine data utilization.
Japan's Science and Technology Agency (JST) will adopt these buoys in its "Co-Creation for Ocean Industry (COI-NEXT)" program, aiming for solutions to marine environment conservation and food security challenges. Buoys will also be provided for the "Nagasaki BLUE Economy: Aquaculture Industrialization Co-Creation Hub for Sustainable Seafood Production," to support a more sustainable future.
Roles of Each Company:
|
Kyocera |
- Manufacturing and supplying smart buoys - Development, supply, and maintenance of cloud applications |
|
Nitto Seimo |
- Buoy installation and retrieval (including mooring design) - Regular maintenance and inspections |
Features of the Smart Buoy:
1. Tidal Power Generation System Unaffected by Weather Conditions
Developed in collaboration with Nagasaki University, the buoy includes a tidal power generation system that utilizes ocean currents to rotate an onboard turbine, generating electricity. Even with weak currents*2, the system can generate power and store it in an onboard battery, ensuring stable long-term data collection.
2. Communication Modules and Sensors for Comprehensive Ocean Data Collection
The buoy is equipped with Kyocera's communication modules, which transmit sensor data every five minutes. Internal sensors collect information such as internal temperature, humidity, acceleration, motor rotation speed, battery level, GPS location, and signal strength. Additionally, external sensors*3 can measure a wide range of oceanographic data, such as current speed and direction, salinity, chlorophyll concentration, turbidity, dissolved oxygen (DO), and water temperature. This flexibility allows customers to select sensors that best suit their specific data collection needs, empowering them with control over their data.
3. Real-time Data Monitoring and Anomaly Alerts from the Cloud
Ocean data is monitored in real-time through a dedicated cloud application alongside the buoy. If an anomaly is detected, users can receive email alerts, enabling rapid response to changes in the marine environment without continuous attention.
*2 Requires a current speed of at least 1 knot for power generation.
*3 Up to two external sensors from JFE Advantech Co., Ltd. can be connected simultaneously.
Comment from Prof. Daisaku Sakaguchi, Dean of the Faculty of Engineering, Nagasaki University:
"In recent years, the demand for ocean data collection has been increasing, mainly due to the impact of red tide on aquaculture in Japan. At Nagasaki University, we installed this system off the coast of Itsuwa Town, Amakusa City, on September 26, 2024, to collect fundamental data for red tide prediction."
This development is poised to significantly impact fisheries, marine conservation, and many other fields. From aquaculture to environmental research, the potential applications of this system are vast, promising to contribute to solving a wide range of both social and environmental issues.
For more information on the service, please visit Kyocera's website (Japanese only):
https://www.kyocera.co.jp/prdct/smartbuoy/