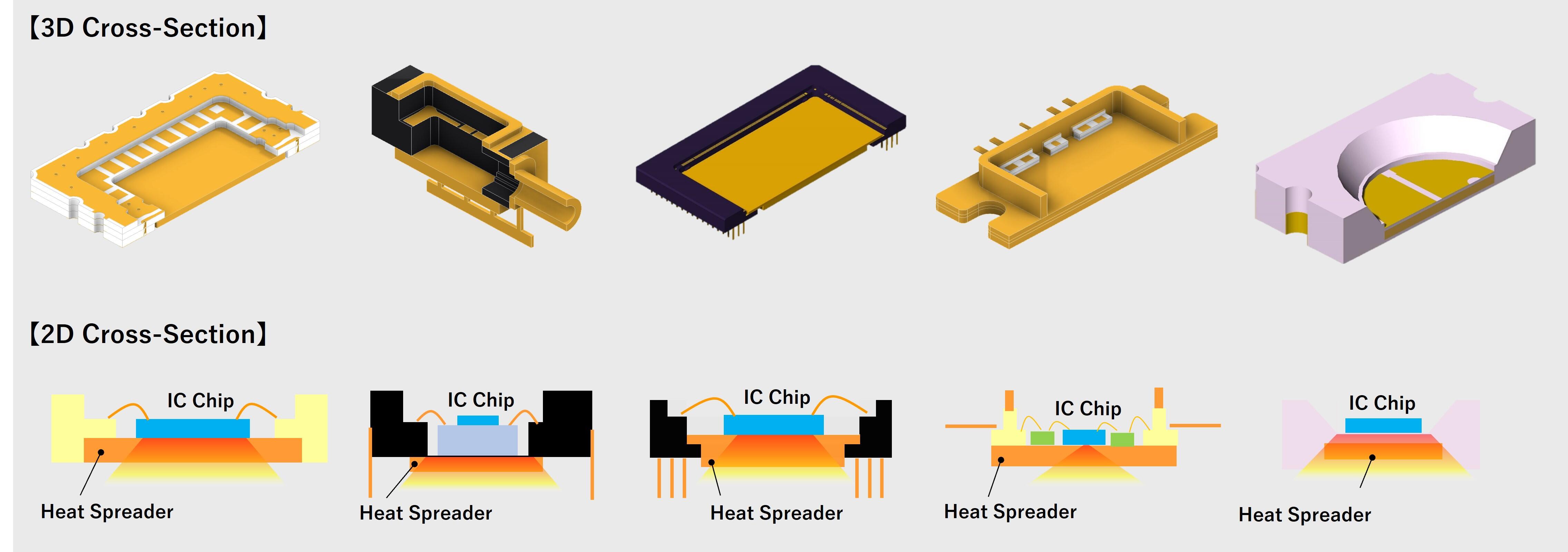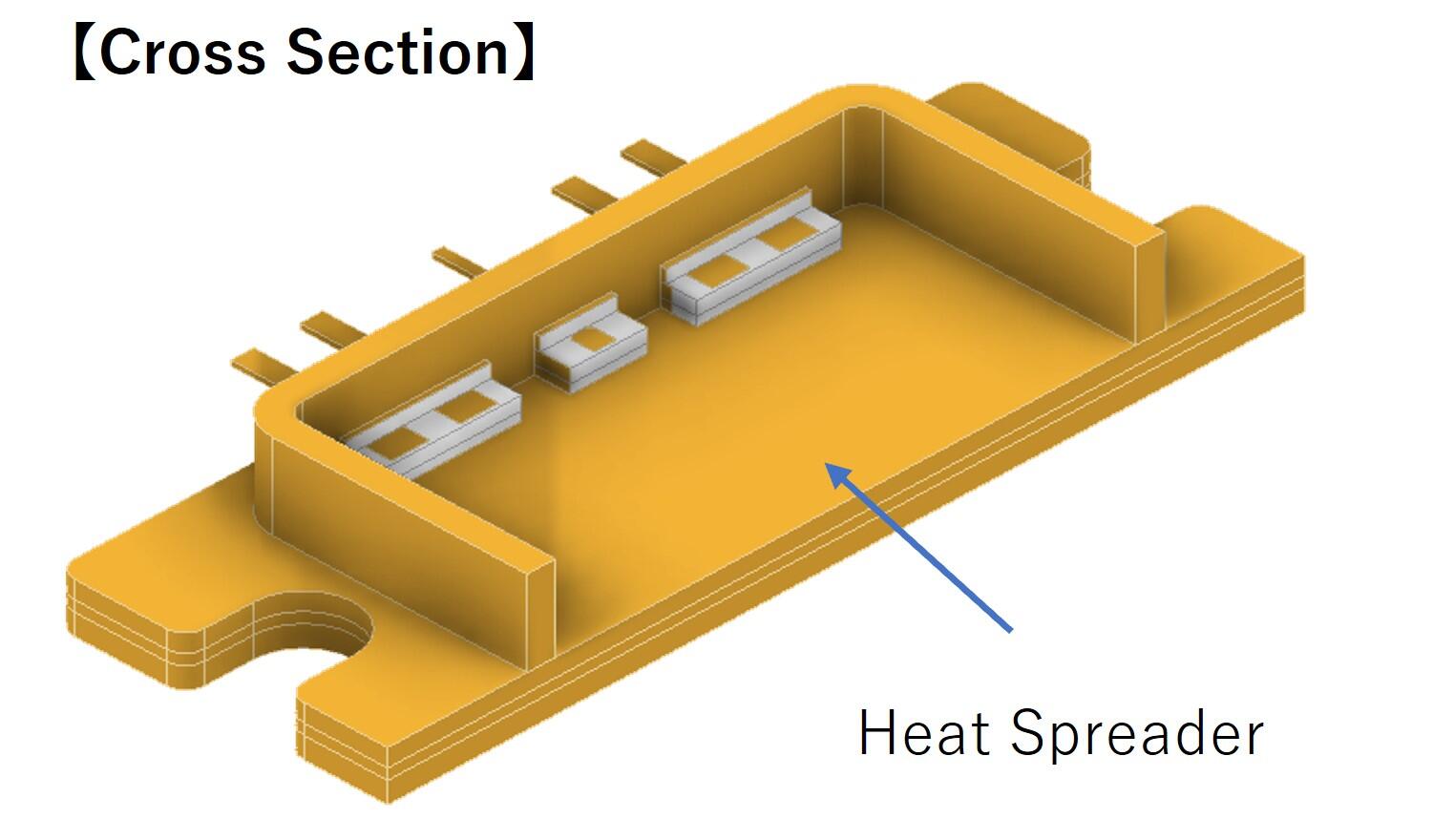
One of the key functions of a package is to dissipate heat generated by the device efficiently. Devices with high power output may require a heat spreader. Kyocera has developed advanced technologies to bond highly thermally conductive metals, such as copper, onto ceramics, creating IC packages that offer superior thermal performance.
Material Properties: Heat Spreader
※O.F.H.C.:Oxygen Free High Conductivity

(*)CTE of CuMo, CPC141, and CPC232 may vary depending on the material's rolled direction.
(**)Thermal resistance is calculated on the conditions below.
Heat source: 1.0 x 1.0 mm; heat spreader thickness: 1.0 mm; bonding material loss not included.
Click here for a simplified formula to calculate thermal resistance.
(**)Thermal resistance is calculated on the conditions below.
Heat source: 1.0 x 1.0 mm; heat spreader thickness: 1.0 mm; bonding material loss not included.
Click here for a simplified formula to calculate thermal resistance.
- The material properties above represent typical values and are subject to change.
- "CPC" is a registered trademark of A.L.M.T. Corp.
(CPC: Laminated heat dissipation structure with Cu layers on top and bottom, CuMo in between (Cu -CuMo-Cu). - "KYCM" and "CM 360" are Kyocera's proprietary materials.
- "KYCM" is a registered trademark of Kyocera Corporation in Japan and China.
Heat Spreader Characteristics
The chart below shows the relationship between thermal conductivity and CTE in various heat spreader materials.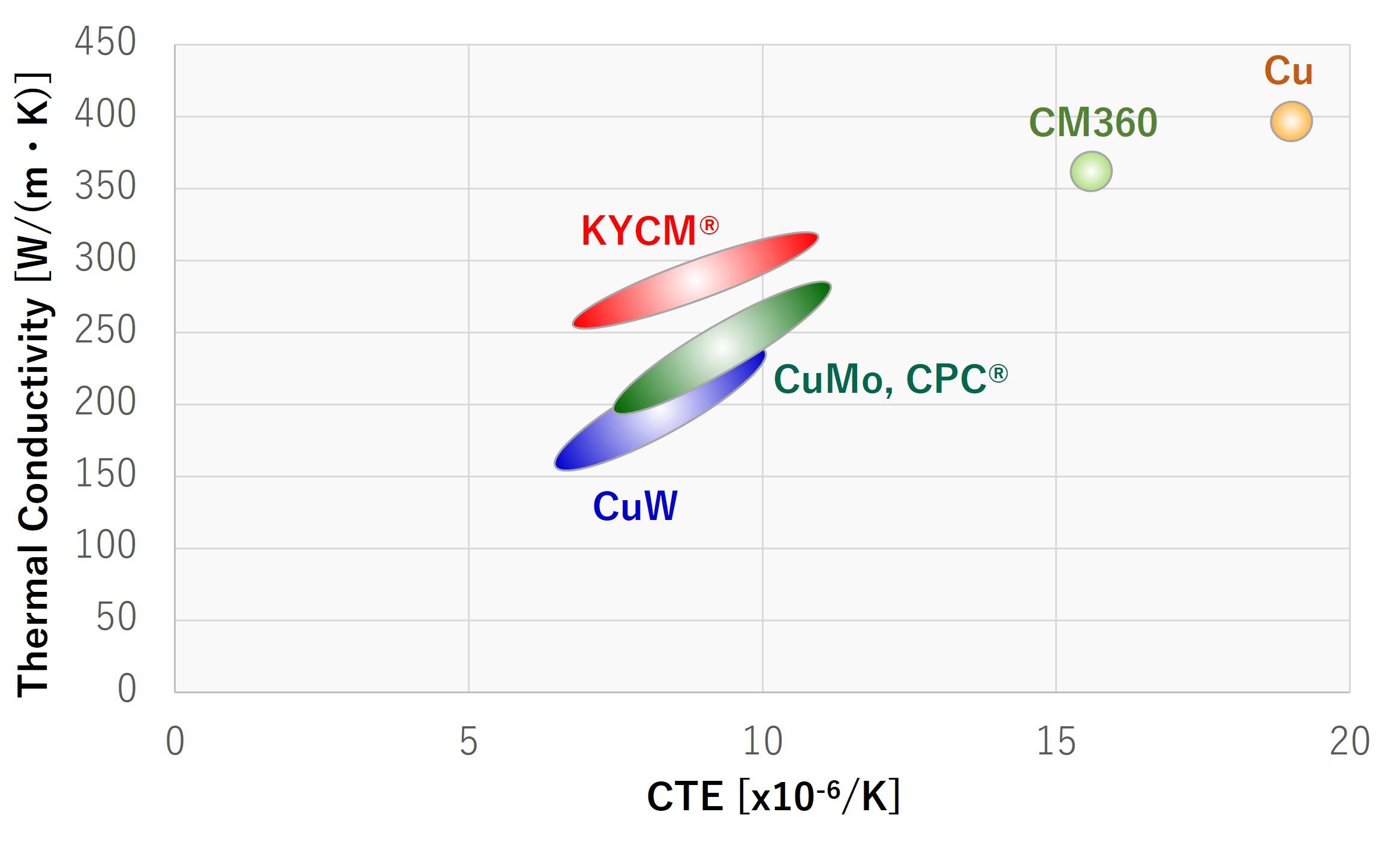
Examples of IC Packages with Heat Spreaders
The illustration below shows examples of IC packages incorporating heat spreaders. Other structures can also be manufactured using various materials. Please contact us for details.