Multi-Magnification Optical Units
Multi-Magnification Optical Units

-
Two (or more) different magnifications in one optical system.
Suitable for rough positioning of object by low magnification, and precise positioning by high magnification.
Example: Dual view optical units
Used for applications such as flip-chip bonding machines.
Enables measurement of the bonding position from upper view and lower view at once with a high degree of accuracy.
fθ Lenses
-
Used for applications such as constant velocity scanning of laser beams with polygon mirrors. When the rotational scanning converts into the linear scanning, it is expressed by the relation "y=f×θ", therefore it is called a f×θ=fθ(f- theta) lens.
Infrared (IR) Lenses

-
Mass-production of silicon and germanium lenses is avalable for infrared sensor and camera applications. Prototype production of molded chalcogenide glass lenses is also available (lower right image). Infrared lenses are used as components in thermal measurement devices, automotive driving safety systems etc.
Possible shapes and diameter of lensShape Bi-convex lens, Bi-concave lens
Convex lens, Concave lens,
Meniscus lensDiameter 5 to 180mm
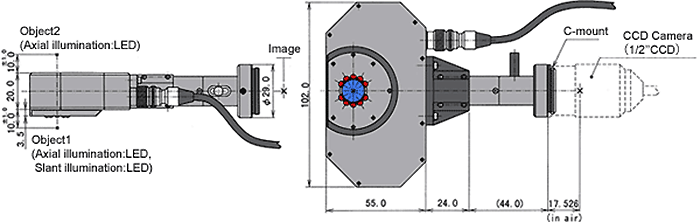
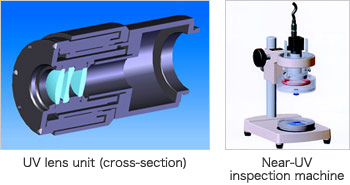
UV Lens Units

-
UV lenses enable monitoring of invisible scratches, particles, or stains on transparent or metal surfaces by using scatter characteristics of UV light.
Specifications
| Magnification | : | 0.2x to 0.6x |
| Effective F-no. | : | 7.4 to 10.2 |
| Image-object distance | : | 176.1 to 105.1mm |
| Working distance | : | 132.0 to 51.3mm |
| TV distortion | : | 0.1% or less |
| Monitor resolution power | : | 1000 TV lines or over |
| Depth of field | : | ±7mm(0.2x) to ±1mm(0.6x) |
| Wave length | : | 320 to 420nm (365nm <BASIC>) |
| Image field size (max) | : | 1/2 inches |
| Mount type | : | C-mount |
| Dimensions | : | φ36 x 26.6mm (0.2x) to 36.3mm (0.6x) |